A cassette of N-terminal amino acids of histone H2B are required for efficient cell survival, DNA repair and Swi/Snf binding in UV irradiated yeast
- PMID: 20007597
- PMCID: PMC2836547
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1074
A cassette of N-terminal amino acids of histone H2B are required for efficient cell survival, DNA repair and Swi/Snf binding in UV irradiated yeast
Abstract
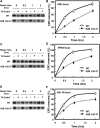
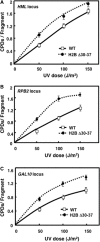
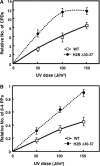
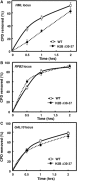
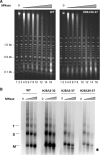
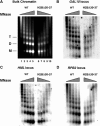
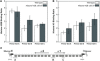
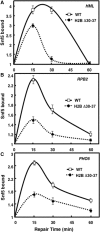
The highly charged histone N-terminal domains are engaged in inter- and intra-nucleosomal interactions, and contain a host of sites used for posttranslational modification. We have studied the effect of deleting residues 30-37 from the N-terminal domain of histone H2B in yeast cells, on nucleotide excision repair (NER) following UV irradiation, as these cells are quite sensitive to UV. We find that H2B Delta30-37 cells exhibit reduced NER efficiency at three specific chromatin loci: the transcriptionally active, RPB2 locus; the transcriptionally silenced, nucleosome-loaded HML locus; and the transcriptionally repressed, non-silenced, GAL10 locus. Nuclease digestion studies indicate that H2B Delta30-37 chromatin has increased nucleosome accessibility and/or nucleosome mobility. In addition, H2B Delta30-37 mutants acquire more DNA damage, compared to wt cells, following the same dose of UV radiation. Reducing the level of damage in H2B Delta30-37 cells to match that of wt cells restores the NER rate to wt levels in the RPB2 and GAL10 loci, but NER efficiency remains low in the silenced HML locus. Interestingly, recruitment of Snf5 to the HML locus is reduced in H2B Delta30-37 cells and more transient following UV irradiation. This may reflect a lower binding affinity of the SWI/SNF complex to H2B Delta30-37 nucleosomes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Histone H3 Lys79 methylation is required for efficient nucleotide excision repair in a silenced locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(5):1690-700. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp003. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19155276 Free PMC article.
-
A single amino acid change in histone H4 enhances UV survival and DNA repair in yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jun;36(11):3857-66. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn311. Epub 2008 May 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18508805 Free PMC article.
-
Rad4-Rad23 interaction with SWI/SNF links ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling with nucleotide excision repair.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Oct;13(10):902-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1152. Epub 2006 Oct 1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 17013386
-
Assays for chromatin remodeling during nucleotide excision repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Methods. 2009 May;48(1):19-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.03.017. Epub 2009 Mar 29. Methods. 2009. PMID: 19336254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone acetylation, chromatin remodelling and nucleotide excision repair: hint from the study on MFA2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Cell Cycle. 2005 Aug;4(8):1043-5. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.8.1928. Epub 2005 Aug 21. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 16082210 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin structure following UV-induced DNA damage-repair or death?Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(11):8063-85. doi: 10.3390/ijms12118063. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22174650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin and transcription in yeast.Genetics. 2012 Feb;190(2):351-87. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.132266. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22345607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleosome Histone Tail Conformation and Dynamics: Impacts of Lysine Acetylation and a Nearby Minor Groove Benzo[a]pyrene-Derived Lesion.Biochemistry. 2017 Apr 11;56(14):1963-1973. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b01208. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28304160 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging roles of ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzymes in nucleotide excision repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(9):11954-11973. doi: 10.3390/ijms130911954. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23109894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational analysis of reciprocal association of metabolism and epigenetics in the budding yeast: a genome-scale metabolic model (GSMM) approach.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 3;9(11):e111686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111686. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25365344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1997;389:251–260. - PubMed
-
- Zheng C, Hayes JJ. Intra- and inter-nucleosomal protein-DNA interactions of the core histone tail domains in a model system. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:24217–24224. - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Allis CD, Jenuwein T, Reinberg D, Caparros ML, editors. Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

