Gene silencing by cell-penetrating, sequence-selective and nucleic-acid hydrolyzing antibodies
- PMID: 20007602
- PMCID: PMC2836572
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1145
Gene silencing by cell-penetrating, sequence-selective and nucleic-acid hydrolyzing antibodies
Abstract
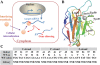
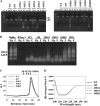
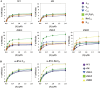
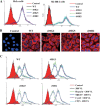
Targeting particular mRNAs for degradation is a fascinating approach to achieve gene silencing. Here we describe a new gene silencing tool exploiting a cell-penetrating, nucleic-acid hydrolyzing, single-domain antibody of the light-chain variable domain, 3D8 VL. We generated a synthetic library of 3D8 VL on the yeast surface by randomizing residues located in one of two beta-sheets. Using 18-bp single-stranded nucleic acids as target substrates, including the human Her2/neu-targeting sequence, we selected 3D8 VL variants that had approximately 100-1000-fold higher affinity and approximately 2-5-fold greater selective hydrolyzing activity for target substrates than for off targets. 3D8 VL variants efficiently penetrated into living cells to be accumulated in the cytosol and selectively decreased the amount of target sequence-carrying mRNAs as well as the proteins encoded by these mRNAs with minimal effects on off-target genes. In particular, one 3D8 VL variant targeting the Her2 sequence showed more efficient downregulation of Her2 expression than a small-interfering RNA targeting the same Her2 sequence, resulting in apoptotic cell death of Her2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Our results demonstrate that cell-penetrating 3D8 VL variants with sequence-selective, nucleic-acid-hydrolyzing activity can selectively degrade target mRNAs in the cytosol, providing a new gene silencing tool mediated by antibody.
Figures


References
-
- Scherer LJ, Rossi JJ. Approaches for the sequence-specific knockdown of mRNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003;21:1457–1465. - PubMed
-
- Tafech A, Bassett T, Sparanese D, Lee CH. Destroying RNA as a therapeutic approach. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006;13:863–881. - PubMed
-
- Cullen BR. Enhancing and confirming the specificity of RNAi experiments. Nat. Methods. 2006;3:677–681. - PubMed
-
- Makarov AA, Ilinskaya ON. Cytotoxic ribonucleases: molecular weapons and their targets. FEBS Lett. 2003;540:15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

