Glucuronidation of psilocin and 4-hydroxyindole by the human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases
- PMID: 20007669
- PMCID: PMC2835393
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.109.031138
Glucuronidation of psilocin and 4-hydroxyindole by the human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases
Abstract
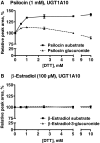
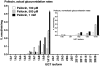
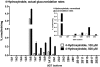
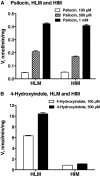
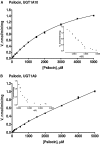
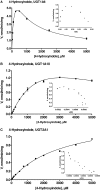
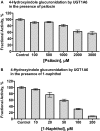
We have examined the glucuronidation of psilocin, a hallucinogenic indole alkaloid, by the 19 recombinant human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) of subfamilies 1A, 2A, and 2B. The glucuronidation of 4-hydroxyindole, a related indole that lacks the N,N-dimethylaminoethyl side chain, was studied as well. UGT1A10 exhibited the highest psilocin glucuronidation activity, whereas the activities of UGTs 1A9, 1A8, 1A7, and 1A6 were significantly lower. On the other hand, UGT1A6 was by far the most active enzyme mediating 4-hydroxyindole glucuronidation, whereas the activities of UGTs 1A7-1A10 toward 4-hydroxyindole resembled their respective psilocin glucuronidation rates. Psilocin glucuronidation by UGT1A10 followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics in which psilocin is a low-affinity high-turnover substrate (K(m) = 3.8 mM; V(max) = 2.5 nmol/min/mg). The kinetics of psilocin glucuronidation by UGT1A9 was more complex and may be best described by biphasic kinetics with both intermediate (K(m1) = 1.0 mM) and very low affinity components. The glucuronidation of 4-hydroxyindole by UGT1A6 exhibited higher affinity (K(m) = 178 microM) and strong substrate inhibition. Experiments with human liver and intestinal microsomes (HLM and HIM, respectively) revealed similar psilocin glucuronidation activity in both samples, but a much higher 4-hydroxyindole glucuronidation rate was found in HLM versus HIM. The expression levels of UGTs 1A6-1A10 in different tissues were studied by quantitative real-time-PCR, and the results, together with the activity assays findings, suggest that whereas psilocin may be subjected to extensive glucuronidation by UGT1A10 in the small intestine, UGT1A9 is likely the main contributor to its glucuronidation once it has been absorbed into the circulation.
Figures
References
-
- Anastos N, Barnett NW, Pfeffer FM, Lewis SW. (2006) Investigation into the temporal stability of aqueous standard solutions of psilocin and psilocybin using high performance liquid chromatography. Sci Justice 46:91–96 - PubMed
-
- Bjornstad K, Hulten P, Beck O, Helander A. (2009) Bioanalytical and clinical evaluation of 103 suspected cases of intoxications with psychoactive plant materials. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 47:566–572 - PubMed
-
- Bowalgaha K, Elliot DJ, Mackenzie PI, Knights KM, Swedmark S, Miners JO. (2005) S-Naproxen and desmethylnaproxen glucuronidation by human liver microsomes and recombinant human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT): role of UGT2B7 in the elimination of naproxen. Br J Clin Pharmacol 60:423–433 - PMC - PubMed
-
- El-Bachá RS, Leclerc S, Netter P, Magdalou J, Minn A. (2000) Glucuronidation of apomorphine. Life Sci 67:1735–1745 - PubMed
-
- Fisher MB, Campanale K, Ackermann BL, VandenBranden M, Wrighton SA. (2000) In vitro glucuronidation using human liver microsomes and the pore-forming peptide alamethicin. Drug Metab Dispos 28:560–566 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

