Identification and functional analysis of PCNA1 and PCNA-like1 genes of Phaseolus coccineus
- PMID: 20007687
- PMCID: PMC2814116
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erp354
Identification and functional analysis of PCNA1 and PCNA-like1 genes of Phaseolus coccineus
Abstract
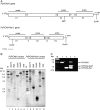
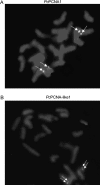
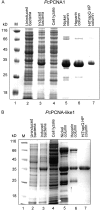
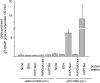
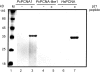
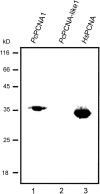
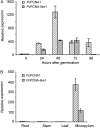
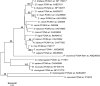
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is an essential factor in DNA replication and in many other processes in eukaryotic cells. Genetic analysis of Phaseolus coccineus showed the presence of at least two PCNA-like genes in the runner bean genome. Two PCNA genes have previously been found in a few plant species including Arabidopsis, tobacco, and maize. In these species, genes were nearly identical. Two cDNAs of P. coccineus PCNA (PcPCNA1 and PcPCNA-like1) have been identified that differ distinctly from each other. Interestingly, both the genetic organization of PcPCNA1 and PcPCNA-like1 genes and their expression patterns were similar, but these were the only similarities between these genes and their products. The identity between PcPCNA1 and PcPCNA-like1 at the amino acid level was only 54%, with PcPCNA-like1 lacking motifs that are crucial for the activity typical of PCNA. Consequently, these two proteins showed different properties. PcPCNA1 behaved like a typical PCNA protein: it formed a homotrimer and stimulated the activity of human DNA polymerase delta. In addition, PcPCNA1 interacted with a p21 peptide and was recognized by an anti-human PCNA monoclonal antibody PC10. By contrast, PcPCNA-like1 was detected as a monomer and was unable to stimulate the DNA polymerase delta activity. PcPCNA-like1 also could not interact with p21 and was not recognized by the PC10 antibody. Our results suggest that PcPCNA-like1 either is unable to function alone and therefore might be a component of the heterotrimeric PCNA ring or may have other, yet unknown functions. Alternatively, the PcPCNA-like1 gene may represent a pseudogene.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular cloning of Phaseolus vulgaris cDNA encoding proliferating cell nuclear antigen.J Plant Physiol. 2007 Feb;164(2):209-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2006.04.009. Epub 2006 Jun 13. J Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 16777262
-
Expression of two genes encoding gibberellin 2- and 3-oxidases in developing seeds of Phaseolus coccineus.Plant Cell Physiol. 2005 Jul;46(7):1116-24. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pci124. Epub 2005 May 13. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15894806
-
The proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) gene family in Zea mays is composed of two members that have similar expression programmes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Jul 17;1353(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(97)00072-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997. PMID: 9256057
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): a key factor in DNA replication and cell cycle regulation.Ann Bot. 2011 May;107(7):1127-40. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcq243. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Ann Bot. 2011. PMID: 21169293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional similarities of prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerase sliding clamps.Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Sep 25;23(18):3613-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.18.3613. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995. PMID: 7478986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biological activity of Arabidopsis flap endonuclease 1 (FEN1) is modulated by nuclear factors that inhibit its aggregation.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 May 16;25(1):648. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06671-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40380113 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating DNA replication in plants.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Dec 1;4(12):a010140. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a010140. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 23209151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis thaliana: proliferating cell nuclear antigen 1 and 2 possibly form homo- and hetero-trimeric complexes in the plant cell.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Jul;8(7):e24837. doi: 10.4161/psb.24837. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23656863 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin (Trxo1) interacts with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and its overexpression affects the growth of tobacco cell culture.Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:688-700. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.018. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28183062 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic effect and mechanism of four ionic liquids on seedling taproots of Arabidopsis thaliana.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 May;25(15):14703-14712. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1621-2. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29532385
References
-
- Abbo S, Miller T, King I. Primed-induced in situ hybridization to plant chromosomes. Genome. 1993;36:815–817. - PubMed
-
- Anderson H, Vonarx EJ, Pastushok L, et al. Arabidopsis thaliana Y-family DNA polymerase η catalyses translesion synthesis and interacts functionally with PCNA2. The Plant Journal. 2008;55:895–908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

