MicroRNA-15b modulates cellular ATP levels and degenerates mitochondria via Arl2 in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes
- PMID: 20007690
- PMCID: PMC2836096
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082610
MicroRNA-15b modulates cellular ATP levels and degenerates mitochondria via Arl2 in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes
Abstract
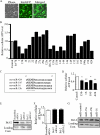
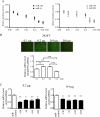
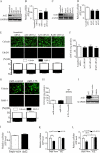
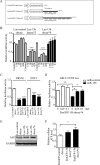
MicroRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) are small, non-coding RNAs that modulate mRNA stability and post-transcriptional translation. A growing body of evidence indicates that specific miRNAs can affect the cellular function of cardiomyocytes. In the present study, miRNAs that are highly expressed in the heart were overexpressed in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes, and cellular ATP levels were assessed. As a result, miR-15b, -16, -195, and -424, which have the same seed sequence, the most critical determinant of miRNA targeting, decreased cellular ATP levels. These results suggest that these miRNAs could specifically down-regulate the same target genes and consequently decrease cellular ATP levels. Through a bioinformatics approach, ADP-ribosylation factor-like 2 (Arl2) was identified as a potential target of miR-15b. It has already been shown that Arl2 localizes to adenine nucleotide transporter 1, the exchanger of ADP/ATP in mitochondria. Overexpression of miR-15b, -16, -195, and -424 suppressed the activity of a luciferase reporter construct fused with the 3'-untranslated region of Arl2. In addition, miR-15b overexpression decreased Arl2 mRNA and protein expression levels. The effects of Arl2 siRNA on cellular ATP levels were the same as those of miR-15b, and the expression of Arl2 could restore ATP levels reduced by miR-15b. A loss-of-function study of miR-15b resulted in increased Arl2 protein and cellular ATP levels. Electron microscopic analysis revealed that mitochondria became degenerated in cardiomyocytes that had been transduced with miR-15b and Arl2 siRNA. The present results suggest that miR-15b may decrease mitochondrial integrity by targeting Arl2 in the heart.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

