The insulin-like growth factor-1 binding protein acid-labile subunit alters mesenchymal stromal cell fate
- PMID: 20007694
- PMCID: PMC2836075
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.041913
The insulin-like growth factor-1 binding protein acid-labile subunit alters mesenchymal stromal cell fate
Abstract
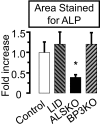
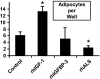
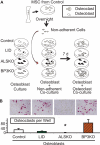
Age-related osteoporosis is accompanied by an increase in marrow adiposity and a reduction in serum insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and the binding proteins that stabilize IGF-1. To determine the relationship between these proteins and bone marrow adiposity, we evaluated the adipogenic potential of marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) from mice with decreased serum IGF-1 due to knockdown of IGF-1 production by the liver or knock-out of the binding proteins. We employed 10-16-week-old, liver-specific IGF-1-deficient, IGFBP-3 knock-out (BP3KO) and acid-labile subunit knock-out (ALSKO) mice. We found that expression of the late adipocyte differentiation marker peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma was increased in marrow isolated from ALSKO mice. When induced with adipogenic media, MSC cultures from ALSKO mice revealed a significantly greater number of differentiated adipocytes compared with controls. MSCs from ALSKO mice also exhibited decreased alkaline-phosphatase positive colony size in cultures that were stimulated with osteoblast differentiation media. These osteoblast-like cells from ALSKO mice failed to induce osteoclastogenesis of control cells in co-culture assays, indicating that impairment of IGF-1 complex formation with ALS in bone marrow alters cell fate, leading to increased adipogenesis.
Figures

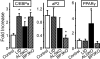
References
-
- Prockop D. J. (1997) Science 276, 71–74 - PubMed
-
- Boyle W. J., Simonet W. S., Lacey D. L. (2003) Nature 423, 337–342 - PubMed
-
- Nuttall M. E., Patton A. J., Olivera D. L., Nadeau D. P., Gowen M. (1998) J. Bone Miner. Res. 13, 371–382 - PubMed
-
- Meunier P., Aaron J., Edouard C., Vignon G. (1971) Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 80, 147–154 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AR054919/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054919/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR055141/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054604/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR055141/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR053853/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR053853/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG002331/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AR045433/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR045433/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG02331/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AR054604/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG002331/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

