Cdc42p is activated during vacuole membrane fusion in a sterol-dependent subreaction of priming
- PMID: 20007700
- PMCID: PMC2836034
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.074609
Cdc42p is activated during vacuole membrane fusion in a sterol-dependent subreaction of priming
Abstract
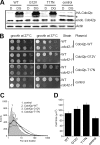
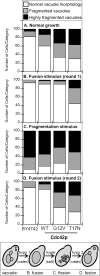
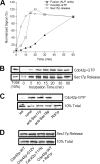
Cdc42p is a Rho GTPase that initiates signaling cascades at spatially defined intracellular sites for many cellular functions. We have previously shown that Cdc42p is localized to the yeast vacuole where it initiates actin polymerization during membrane fusion. Here we examine the activation cycle of Cdc42p during vacuole membrane fusion. Expression of either GTP- or GDP-locked Cdc42p mutants caused several morphological defects including enlarged cells and fragmented vacuoles. Stimulation of multiple rounds of fusion enhanced vacuole fragmentation, suggesting that cycles of Cdc42p activation, involving rounds of GTP binding and hydrolysis, are required to propagate Cdc42p signaling. We developed an assay to directly examine Cdc42p activation based on affinity to a probe derived from the p21-activated kinase effector, Ste20p. Cdc42p was rapidly activated during vacuole membrane fusion, which kinetically coincided with priming subreaction. During priming, Sec18p ATPase activity dissociates SNARE complexes and releases Sec17p, however, priming inhibitors such as Sec17p and Sec18p ligands did not block Cdc42p activation. Therefore, Cdc42p activation seems to be a parallel subreaction of priming, distinct from Sec18p activity. Specific mutants in the ergosterol synthesis pathway block both Sec17p release and Cdc42p activation. Taken together, our results define a novel sterol-dependent subreaction of vacuole priming that activates cycles of Cdc42p activity to facilitate membrane fusion.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cdc42p and Rho1p are sequentially activated and mechanistically linked to vacuole membrane fusion.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Mar 26;394(1):64-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.102. Epub 2010 Feb 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20171953
-
Stimulation of actin polymerization by vacuoles via Cdc42p-dependent signaling.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 19;282(42):30466-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704117200. Epub 2007 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17726018
-
Cdc42p functions at the docking stage of yeast vacuole membrane fusion.EMBO J. 2001 Oct 15;20(20):5657-65. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.20.5657. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11598009 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast homotypic vacuole fusion: a window on organelle trafficking mechanisms.Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:247-75. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.247. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10966459 Review.
-
V-ATPase, ScNhx1p and yeast vacuole fusion.J Genet Genomics. 2012 Apr 20;39(4):167-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2012.02.001. Epub 2012 Feb 10. J Genet Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22546538 Review.
Cited by
-
The MAP kinase Slt2 is involved in vacuolar function and actin remodeling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants affected by endogenous oxidative stress.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Oct;79(20):6459-71. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01692-13. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23956390 Free PMC article.
-
Plant vacuole morphology and vacuolar trafficking.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Sep 24;5:476. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00476. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25309565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wsp1 is downstream of Cin1 and regulates vesicle transport and actin cytoskeleton as an effector of Cdc42 and Rac1 in Cryptococcus neoformans.Eukaryot Cell. 2012 Apr;11(4):471-81. doi: 10.1128/EC.00011-12. Epub 2012 Feb 10. Eukaryot Cell. 2012. PMID: 22327008 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp70 chaperones, Ssa1 and Ssa2, limit poly(A) binding protein aggregation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 20:2025.01.17.633617. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.17.633617. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Mol Biol Cell. 2025 Jun 1;36(6):ar66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E25-01-0027. PMID: 39896508 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Hsp70 chaperones, Ssa1 and Ssa2, limit poly(A) binding protein aggregation.Mol Biol Cell. 2025 Jun 1;36(6):ar66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E25-01-0027. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 40202836
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

