FGF2-activated ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase enhances Runx2 acetylation and stabilization
- PMID: 20007706
- PMCID: PMC2823497
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.055053
FGF2-activated ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase enhances Runx2 acetylation and stabilization
Abstract
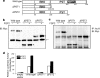
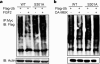
Runx2 is a key transcription factor regulating osteoblast differentiation and skeletal morphogenesis, and FGF2 is one of the most important regulators of skeletal development. The importance of the ERK mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathway in cranial suture development was demonstrated by the findings that the inhibition of FGF/FGF receptor (FGFR) signaling by a MEK blocker prevents the premature suture closure caused by an Fgfr2 mutation in mice. We previously demonstrated that ERK activation does not affect Runx2 gene expression but that it stimulates Runx2 transcriptional activity. However, the molecular mechanism underlying Runx2 activation by FGF/FGFR or ERK was still unclear. In this study, we found that FGF2 treatment increased the protein level of exogenously overexpressed Runx2 and that this increase is reversed by ERK inhibitors. In contrast, overexpression of constitutively active MEK strongly increased the Runx2 protein level, which paralleled an increase in Runx2 acetylation. As Runx2 protein phosphorylation mediated by ERK directly correlates with Runx2 protein stabilization, acetylation, and ubiquitination, we undertook to identify the ERK-dependent phosphorylation sites in Runx2. Analysis of two C-terminal Runx2 deletion constructs showed that the middle third of the protein is responsible for ERK-induced stabilization and activation. An in silico analysis of highly conserved ERK targets indicated that there are three relevant serine residues in this domain. Site-directed mutagenesis implicated Ser-301 in for ERK-mediated Runx2 stabilization and acetylation. In conclusion, the FGF2-induced ERK MAP kinase strongly increased the Runx2 protein level through an increase in acetylation and a decrease in ubiquitination, and these processes require the phosphorylation of Runx2 Ser-301 residue.
Figures

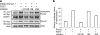

Similar articles
-
BMP2-activated Erk/MAP kinase stabilizes Runx2 by increasing p300 levels and histone acetyltransferase activity.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 19;285(47):36410-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.142307. Epub 2010 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20851880 Free PMC article.
-
Prolyl isomerase Pin1-mediated conformational change and subnuclear focal accumulation of Runx2 are crucial for fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2)-induced osteoblast differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 28;289(13):8828-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.516237. Epub 2014 Feb 7. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24509851 Free PMC article.
-
FGF2 stimulates osteogenic differentiation through ERK induced TAZ expression.Bone. 2014 Jan;58:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.09.024. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Bone. 2014. PMID: 24125755
-
Runx2 trans-activation mediated by the MSX2-interacting nuclear target requires homeodomain interacting protein kinase-3.Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Jul;24(7):1478-97. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0029. Epub 2010 May 19. Mol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20484411 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational Regulation of Runx2 in Bone and Cartilage.J Dent Res. 2009 Aug;88(8):693-703. doi: 10.1177/0022034509341629. J Dent Res. 2009. PMID: 19734454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Osteoblasts.J Bone Metab. 2022 Feb;29(1):1-15. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2022.29.1.1. Epub 2022 Feb 28. J Bone Metab. 2022. PMID: 35325978 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidylarginine deiminase 2 plays a key role in osteogenesis by enhancing RUNX2 stability through citrullination.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 30;14(8):576. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06101-7. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37648716 Free PMC article.
-
Novel application of luciferase assay for the in vitro functional assessment of KAL1 variants in three females with septo-optic dysplasia (SOD).Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 5;417:63-72. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.09.010. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26375424 Free PMC article.
-
ERK acts in parallel to PKCδ to mediate the connexin43-dependent potentiation of Runx2 activity by FGF2 in MC3T3 osteoblasts.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Apr 1;302(7):C1035-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00262.2011. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22277757 Free PMC article.
-
Bone-derived PDGF-BB drives brain vascular calcification in male mice.J Clin Invest. 2023 Dec 1;133(23):e168447. doi: 10.1172/JCI168447. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37815871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levanon D., Negreanu V., Bernstein Y., Bar-Am I., Avivi L., Groner Y. (1994) Genomics 23, 425–432 - PubMed
-
- Ducy P., Zhang R., Geoffroy V., Ridall A. L., Karsenty G. (1997) Cell 89, 747–754 - PubMed
-
- Stein G. S., Lian J. B., van Wijnen A. J., Stein J. L., Montecino M., Javed A., Zaidi S. K., Young D. W., Choi J. Y., Pockwinse S. M. (2004) Oncogene 23, 4315–4329 - PubMed
-
- Mundlos S., Otto F., Mundlos C., Mulliken J. B., Aylsworth A. S., Albright S., Lindhout D., Cole W. G., Henn W., Knoll J. H., Owen M. J., Mertelsmann R., Zabel B. U., Olsen B. R. (1997) Cell 89, 773–779 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

