Structural basis for translation factor recruitment to the eukaryotic/archaeal ribosomes
- PMID: 20007716
- PMCID: PMC2836080
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.068098
Structural basis for translation factor recruitment to the eukaryotic/archaeal ribosomes
Abstract
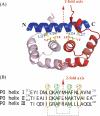
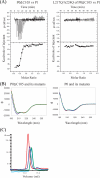
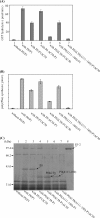
The archaeal ribosomal stalk complex has been shown to have an apparently conserved functional structure with eukaryotic pentameric stalk complex; it provides access to eukaryotic elongation factors at levels comparable to that of the eukaryotic stalk. The crystal structure of the archaeal heptameric (P0(P1)(2)(P1)(2)(P1)(2)) stalk complex shows that the rRNA anchor protein P0 consists of an N-terminal rRNA-anchoring domain followed by three separated spine helices on which three P1 dimers bind. Based on the structure, we have generated P0 mutants depleted of any binding site(s) for P1 dimer(s). Factor-dependent GTPase assay of such mutants suggested that the first P1 dimer has higher activity than the others. Furthermore, we constructed a model of the archaeal 50 S with stalk complex by superposing the rRNA-anchoring domain of P0 on the archaeal 50 S. This model indicates that the C termini of P1 dimers where translation factors bind are all localized to the region between the stalk base of the 50 S and P0 spine helices. Together with the mutational experiments we infer that the functional significance of multiple copies of P1 is in creating a factor pool within a limited space near the stalk base of the ribosome.
Figures




References
-
- Möller W., Maassen J. A. (1986) in Structure, Function, and Genetics of Ribosomes (Hardesty B., Kramer G. eds) pp. 309–325, Springer-Verlag New York Inc., New York
-
- Chandra Sanyal S., Liljas A. (2000) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 10, 633–636 - PubMed
-
- Traut R. R., Dey D., Bochkariov D. E., Oleinikov A. V., Jokhadze G. G., Hamman B., Jameson D. (1995) Biochem. Cell Biol. 73, 949–958 - PubMed
-
- Gudkov A. T. (1997) FEBS Lett. 407, 253–256 - PubMed
-
- Bocharov E. V., Sobol A. G., Pavlov K. V., Korzhnev D. M., Jaravine V. A., Gudkov A. T., Arseniev A. S. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 17697–17706 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

