High-b-value diffusion MR imaging and basal nuclei apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in variant and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- PMID: 20007724
- PMCID: PMC7963959
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1860
High-b-value diffusion MR imaging and basal nuclei apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in variant and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
Abstract
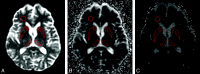
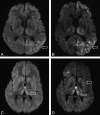
Background and purpose: DWI using a standard b-value of 1000 s/mm(2) has emerged as the most sensitive sequence for the diagnosis of CJD. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether DWI at a high b-value (b = 3000 s/mm(2)) and ADC measurements in the basal nuclei improve the diagnosis of vCJD and sCJD compared with visual assessment of DWI at a standard b-value (b = 1000 s/mm(2)).
Materials and methods: Eight patients with vCJD, 9 patients with sCJD, and 5 healthy volunteers underwent DWI at b = 1000 s/mm(2), and 5 vCJD patients, 4 sCJD patients, and 1 growth hormone-related CJD patient underwent DWI at b = 3000 s/mm(2). Two consultant neuroradiologists performed a visual comparison of the b = 1000 and b = 3000 images. Mean MR SI and ADC values were determined for C, P, and DM thalamus ROIs bilaterally at each b-value. SI ratios for each ROI relative to white matter were calculated.
Results: In 9 out of 10 patients, the higher b-value images were more sensitive to SI change, particularly in cortex and thalamus, with higher SI ratios at b = 3000 in the DM thalamus. For sCJD at b = 1000, we found significantly lower ADC values in the C and P compared with controls (mean C ADC = 587.3 +/- 84.7 mm(2)/s in sCJD patients versus 722.7 +/- 16.6 mm(2)/s in controls; P = .007), and at b = 3000, the differences were more pronounced. In comparison, in vCJD at b = 1000, ADC values were elevated in the Pu (mean Pu ADC = 837.6 +/- 33.0 mm/s(2) in vCJD patients versus 748.0 +/- 17.3 mm/s(2) in controls; P < .001) but failed to reach significance at b = 3000.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that b = 3000 DWI, being more sensitive to slowly diffusing tissue water, is more sensitive to pathology in sCJD than is conventional DWI. High-b-value DWI increases confidence in the radiologic diagnosis of human prion disease.
Figures

References
-
- Shiga Y, Miyazawa K, Sato S, et al. . Diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities as an early diagnostic marker for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 2004;63:443–49 - PubMed
-
- Tschampa HJ, Kallenberg K, Urbach H, et al. . MRI in the diagnosis of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a study on inter-observer agreement. Brain 2005;128:2026–33 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
