Error-prone translesion replication of damaged DNA suppresses skin carcinogenesis by controlling inflammatory hyperplasia
- PMID: 20007784
- PMCID: PMC2799833
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909507106
Error-prone translesion replication of damaged DNA suppresses skin carcinogenesis by controlling inflammatory hyperplasia
Abstract
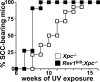
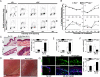
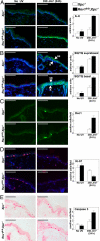
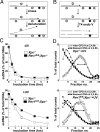
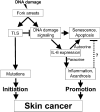
The induction of skin cancer involves both mutagenic and proliferative responses of the epidermis to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is believed that tumor initiation requires the mutagenic replication of damaged DNA by translesion synthesis (TLS) pathways. The mechanistic basis for the induction of proliferation, providing tumor promotion, is poorly understood. Here, we have investigated the role of TLS in the initiation and promotion of skin carcinogenesis, using a sensitive nucleotide excision repair-deficient mouse model that carries a hypomorphic allele of the error-prone TLS gene Rev1. Despite a defect in UV-induced mutagenesis, skin carcinogenesis was accelerated in these mice. This paradoxical phenotype was caused by the induction of inflammatory hyperplasia of the mutant skin that provides strong tumor promotion. The induction of hyperplasia was associated with mild and transient replicational stress of the UV-damaged genome, triggering DNA damage signaling and senescence. The concomitant expression of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is in agreement with an executive role for IL-6 and possibly other cytokines in the autocrine induction of senescence and the paracrine induction of inflammatory hyperplasia. In conclusion, error-prone TLS suppresses tumor-promoting activities of UV light, thereby controlling skin carcinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kundu JK, Surh YJ. Inflammation: Gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat Res. 2008;659:15–30. - PubMed
-
- Mueller MM. Inflammation in epithelial skin tumours: Old stories and new ideas. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:735–744. - PubMed
-
- Melnikova VO, Ananthaswamy HN. Cellular and molecular events leading to the development of skin cancer. Mutat Res. 2005;571:91–106. - PubMed
-
- Lehmann AR, et al. Translesion synthesis: Y-family polymerases and the polymerase switch. DNA Repair. 2007;6:891–899. - PubMed
-
- Gan GN, Wittschieben JP, Wittschieben BØ, Wood RD. DNA polymerase zeta (pol zeta) in higher eukaryotes. Cell Res. 2008;18:174–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

