Electrogenic tuning of the axon initial segment
- PMID: 20007821
- PMCID: PMC2951114
- DOI: 10.1177/1073858409341973
Electrogenic tuning of the axon initial segment
Abstract
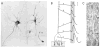
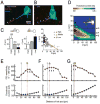
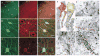
Action potentials (APs) provide the primary means of rapid information transfer in the nervous system. Where exactly these signals are initiated in neurons has been a basic question in neurobiology and the subject of extensive study. Converging lines of evidence indicate that APs are initiated in a discrete and highly specialized portion of the axon-the axon initial segment (AIS). The authors review key aspects of the organization and function of the AIS and focus on recent work that has provided important insights into its electrical signaling properties. In addition to its main role in AP initiation, the new findings suggest that the AIS is also a site of complex AP modulation by specific types of ion channels localized to this axonal domain.
Figures


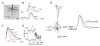
References
-
- Alle H, Geiger JR. Analog signalling in mammalian cortical axons. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008;18:314–20. - PubMed
-
- Araki T, Otani T. Response of single motoneurons to direct stimulation in toad’s spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1955;18:472–85. - PubMed
-
- Bishop PO. Synaptic transmission; an analysis of the electrical activity of the lateral geniculate nucleus in the cat after optic nerve stimulation. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1953;141:362–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

