Alterations in the intraocular cytokine milieu after intravitreal bevacizumab
- PMID: 20007836
- PMCID: PMC2868488
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.09-4065
Alterations in the intraocular cytokine milieu after intravitreal bevacizumab
Abstract
Purpose: Several complications after intravitreal bevacizumab (IVB) treatment have been described including tears of the retinal pigment epithelium and tractional retinal detachment. The etiology of these complications remains unclear. The purpose of this study was to characterize changes in the intraocular levels of inflammatory cytokines after IVB as a possible explanation for these complications.
Methods: Twenty-nine patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) undergoing pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) for vitreous hemorrhage (VH) with IVB pretreatment were prospectively enrolled. Aqueous humor samples were taken at the time of IVB pretreatment and approximately 1 week later at the time of PPV. Multiplex cytokine arrays were used to assay 20 different cytokines. Multivariate general linear regression was performed to determine differences in cytokine levels between the two study visits. Proportional hazards regression was performed to determine the relationship between cytokine levels at PPV and postoperative outcomes.
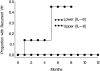
Results: After treatment with IVB, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) concentrations in the aqueous humor decreased (P = 0.0003), whereas the concentrations of IL-8 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta(2) increased after IVB (P < 0.03). The level of IL-8 at the time of PPV was associated with the occurrence of recurrent VH after surgery (hazard ratio, 1.32; P = 0.02).
Conclusions: Alterations in the intraocular inflammatory cytokine milieu occur after IVB injection, possibly as a compensatory mechanism in response to VEGF inhibition. The increased concentrations of inflammatory cytokines after IVB may be clinically significant and may be responsible for some of the complications after IVB.
Figures
References
-
- Aiello LP, Avery RL, Arrigg PG, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1480–1487 - PubMed
-
- Adamis AP, Miller JW, Bernal MT, et al. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the vitreous of eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1994;118:445–450 - PubMed
-
- Watanabe D, Suzuma K, Suzuma I, et al. Vitreous levels of angiopoietin 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2005;139:476–481 - PubMed
-
- Maberley D, Cui JZ, Matsubara JA. Vitreous leptin levels in retinal disease. Eye 2006;20:801–804 - PubMed
-
- Demircan N, Safran BG, Soylu M, Ozcan AA, Sizmaz S. Determination of vitreous interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) levels in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Eye 2006;20:1366–1369 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

