5-HT(1A), SST(1), and SST(2) receptors mediate inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in the submucous plexus of the guinea pig ileum
- PMID: 20007849
- PMCID: PMC2838515
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00438.2009
5-HT(1A), SST(1), and SST(2) receptors mediate inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in the submucous plexus of the guinea pig ileum
Abstract
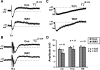
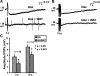
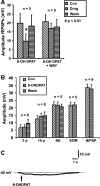
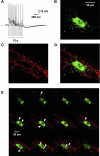
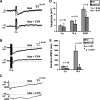
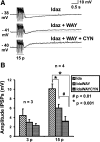
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) immunoreactive neurons are important secretomotor neurons in the submucous plexus. They are the only submucosal neurons to receive inhibitory inputs and exhibit both noradrenergic and nonadrenergic inhibitory synaptic potentials (IPSPs). The former are mediated by alpha(2)-adrenoceptors, but the receptors mediating the latter have not been identified. We used standard intracellular recording, RT-PCR, and confocal microscopy to test whether 5-HT(1A), SST(1), and/or SST(2) receptors mediate nonadrenergic IPSPs in VIP submucosal neurons in guinea pig ileum in vitro. The specific 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist WAY 100135 (1 microM) reduced the amplitude of IPSPs, an effect that persisted in the presence of the alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan (2 microM), suggesting that 5-HT might mediate a component of the IPSPs. Confocal microscopy revealed that there were many 5-HT-immunoreactive varicosities in close contact with VIP neurons. The specific SSTR(2) antagonist CYN 154806 (100 nM) and a specific SSTR(1) antagonist SRA 880 (3 microM) each reduced the amplitude of nonadrenergic IPSPs and hyperpolarizations evoked by somatostatin. In contrast with the other antagonists, CYN 154806 also reduced the durations of nonadrenergic IPSPs. Effects of WAY 100135 and CYN 154806 were additive. RT-PCR revealed gene transcripts for 5-HT(1A), SST(1), and SST(2) receptors in stripped submucous plexus preparations consistent with the pharmacological data. Although the involvement of other neurotransmitters or receptors cannot be excluded, we conclude that 5-HT(1A), SST(1), and SST(2) receptors mediate nonadrenergic IPSPs in the noncholinergic (VIP) secretomotor neurons. This study thus provides the tools to identify functions of enteric neural pathways that inhibit secretomotor reflexes.
Figures
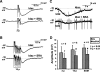

Similar articles
-
5-HT antagonists NAN-190 and SB 269970 block alpha2-adrenoceptors in the guinea pig.Neuroreport. 2009 Feb 18;20(3):325-30. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e3283232caa. Neuroreport. 2009. PMID: 19190523
-
Mucosal stimulation activates secretomotor neurons via long myenteric pathways in guinea pig ileum.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Feb;292(2):G608-14. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00364.2006. Epub 2006 Sep 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17008553
-
ATP participates in three excitatory postsynaptic potentials in the submucous plexus of the guinea pig ileum.J Physiol. 2004 Apr 15;556(Pt 2):571-84. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.060848. Epub 2004 Feb 13. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14966305 Free PMC article.
-
Correlated electrophysiological and histochemical studies of submucous neurons and their contribution to understanding enteric neural circuits.J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Nov;25(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90002-1. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988. PMID: 3066810 Review.
-
Enterotoxins and the enteric nervous system--a fatal attraction.Int J Med Microbiol. 2000 Oct;290(4-5):491-6. doi: 10.1016/S1438-4221(00)80073-9. Int J Med Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11111932 Review.
Cited by
-
Somatostatin as an Active Substance in the Mammalian Enteric Nervous System.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 10;20(18):4461. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184461. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31510021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational simulations and Ca2+ imaging reveal that slow synaptic depolarizations (slow EPSPs) inhibit fast EPSP evoked action potentials for most of their time course in enteric neurons.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Jun 13;18(6):e1009717. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009717. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35696419 Free PMC article.
-
Enteric nervous system: sensory transduction, neural circuits and gastrointestinal motility.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Jun;17(6):338-351. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-0271-2. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32152479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constitutively Elevated Blood Serotonin Is Associated with Bone Loss and Type 2 Diabetes in Rats.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 23;11(2):e0150102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150102. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26907598 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 modulates neurally evoked mucosal chloride secretion in guinea pig small intestine in vitro.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Feb 1;302(3):G352-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00333.2011. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22075777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bornstein JC, Furness JB. Correlated electrophysiological and histochemical studies of submucous neurons and their contribution to understanding enteric neural circuits. J Auton Nerv Syst 25: 1–13, 1988 - PubMed
-
- Chen JJ, Li ZS, Pan H, Murphy DL, Tamir H, Koepsell H, Gershon MD. Maintenance of serotonin in the intestinal mucosa and ganglia of mice that lack the high-affinity serotonin transporter: abnormal intestinal motility and the expression of cation transporters. J Neurosci 21: 6348–6361, 2001 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cooke HJ, Wang YZ, Wray D, O'Dorisio MS, Woltering EA, Coy DH, Murphy WA, Christofi FL, Gosh P, O'Dorisio TM. A multi-tyrosinated sst1/2 receptor preferring somatostatin agonist inhibits reflex and immune-mediated secretion in the guinea pig colon. Regul Pept 114: 51–60, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

