WNT5A expression in ameloblastoma and its roles in regulating enamel epithelium tumorigenic behaviors
- PMID: 20008136
- PMCID: PMC2797904
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090478
WNT5A expression in ameloblastoma and its roles in regulating enamel epithelium tumorigenic behaviors
Abstract
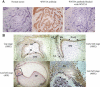
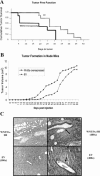
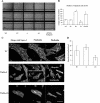
Odontogenic tumors originate from the remains of migrating enamel epithelium after the completion of normal tooth genesis. These enamel epithelium remnants exhibit the ability to recapitulate the events that occur during tooth formation. Several lines of evidence suggest that aberrance in the signaling pathways similar to the ones that are used during tooth development, including the WNT pathway, might be the cause of odontogenic tumorigenesis and maintenance. In this study we demonstrated that WNT5A expression was intense in both the epithelial component of ameloblastomas, the most common epithelial odontogenic tumor, and in this tumor's likely precursor cell, the enamel epithelium located at the cervical loop of normal developing human tooth buds. Additionally, when WNT5A was overexpressed in enamel epithelium cells (LS-8), the clones expressing high levels of WNT5A (S) exhibited characteristics of tumorigenic cells, including growth factor independence, loss of anchorage dependence, loss of contact inhibition, and tumor formation in immunocompromised mice. Moreover, overexpression of WNT5A drastically increased LS-8 cell migration and actin reorganization when compared with controls. Suppression of endogenous WNT5A in LS-8 cells (AS) greatly impaired their migration and AS cells failed to form significant actin reorganization and membrane protrusion was rarely seen. Taken together, our data indicate that WNT5A signaling is important in modulating tumorigenic behaviors of enamel epithelium cells in ameloblastomas.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemical expression of WNT5A and MMPs in odontogenic epithelial tumors and cysts.Acta Histochem. 2015 Oct;117(8):667-74. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2015.10.006. Epub 2015 Nov 7. Acta Histochem. 2015. PMID: 26558991
-
Expression of the stem cell marker, SOX2, in ameloblastoma and dental epithelium.Eur J Oral Sci. 2013 Dec;121(6):509-16. doi: 10.1111/eos.12095. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Eur J Oral Sci. 2013. PMID: 24148099
-
Is podoplanin expression associated with the proliferative activity of ameloblastomas?Oral Dis. 2012 Oct;18(7):673-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2012.01924.x. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Oral Dis. 2012. PMID: 22443371
-
Immunohistochemical biomarkers in ameloblastomas.Acta Odontol Scand. 2016 Nov;74(8):585-590. doi: 10.1080/00016357.2016.1224918. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Acta Odontol Scand. 2016. PMID: 27571891 Review.
-
WNT5A in tumor development and progression: A comprehensive review.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Nov;155:113599. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113599. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36089446 Review.
Cited by
-
SOX2 and BCL-2 Expressions in Odontogenic Keratocyst and Ameloblastoma.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2020 Mar 1;25(2):e283-e290. doi: 10.4317/medoral.23348. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2020. PMID: 31967981 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoexpression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway proteins in ameloblastoma and calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor.J Clin Exp Dent. 2017 Jan 1;9(1):e136-e140. doi: 10.4317/jced.53100. eCollection 2017 Jan. J Clin Exp Dent. 2017. PMID: 28149478 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasizing Ameloblastoma: A 10 Year Clinicopathological Review with an Insight Into Pathogenesis.Head Neck Pathol. 2021 Sep;15(3):967-974. doi: 10.1007/s12105-020-01258-5. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Head Neck Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33394372 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5a regulates Ameloblastoma Cell Migration by modulating Mitochondrial and Cytoskeletal Dynamics.J Cancer. 2020 Jul 11;11(18):5490-5502. doi: 10.7150/jca.46547. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32742496 Free PMC article.
-
Kallikrein 4 and matrix metalloproteinase-20 immunoexpression in malignant, benign and infiltrative odontogenic tumors.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2016 May-Aug;20(2):246-51. doi: 10.4103/0973-029X.185927. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27601817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamamoto Y, Hamamoto N, Nakajima T, Ozawa H. Morphological changes of epithelial rests of Malassez in rat molars induced by local administration of N-methylnitrosourea. Arch Oral Biol. 1998;43:899–906. - PubMed
-
- Philipsen HP, Reichart PA, Ogawa I, Suei Y, Takata T. The inflammatory paradental cyst: a critical review of 342 cases from a literature survey, including 17 new cases from the author's files. J Oral Pathol Med. 2004;33:147–155. - PubMed
-
- Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichert P, Sidransky D. World Health Organization classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of head and neck tumors. IARC Press; Lyon: 2005. pp. 1–430.
-
- Neville BW. Oral and maxillofacial pathology. W.B. Saunders; Philadelphia; Toronto: 2008. pp. 1–984.
-
- Sapp JP, Eversole LR, Wysocki GP. Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology. Mosby; St. Louis: 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

