The absence of interleukin-6 enhanced arsenite-induced renal injury by promoting autophagy of tubular epithelial cells with aberrant extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation
- PMID: 20008137
- PMCID: PMC2797868
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090146
The absence of interleukin-6 enhanced arsenite-induced renal injury by promoting autophagy of tubular epithelial cells with aberrant extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation
Abstract
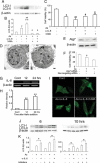
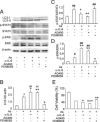
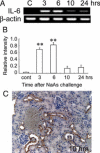
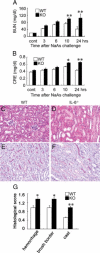
Sodium arsenite (NaAs)-induced autophagic cell death (ACD) of a mouse renal tubular epithelial cell line (mProx24), which expresses enhanced levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), was reduced by the suppression of autophagy by 3-methyladenine or Atg7 knockdown. The inhibition of the IL-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signal pathway by anti-IL-6 antibody or a Jak2 inhibitor (AG490) exaggerated ACD of mProx24 cells after NaAs challenge, attenuating STAT3 activation and reciprocally enhancing extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation. In contrast, an ERK inhibitor, PD98059, reduced NaAs-induced ACD in mProx24 cells. Subcutaneous injection of NaAs (12.5 mg/kg) into BALB/c (wild-type) mice enhanced intrarenal expression of IL-6, mainly produced by tubular cells, and caused severe renal injury characterized by hemorrhages, acute tubular necrosis, cast formation, and brush border disappearance, with increases in serum urea nitrogen (blood urea nitrogen) and creatinine levels. In addition, IL-6-deficient (IL-6(-/-)) mice exhibited exaggerated histopathological changes with higher blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels. Moreover, in IL-6(-/-) mice treated with NaAs, ACD in renal tubular cells was significantly augmented, along with diminished STAT3 activation and reciprocal enhancement of ERK signaling, compared with wild-type mice. Finally, the administration of exogenous IL-6 into wild-type mice significantly reduced NaAs-induced ACD along with diminished ERK activation and eventually alleviated acute renal dysfunction. Thus, IL-6/STAT3 signal pathway could inhibit ERK activation, a crucial step for ACD, eventually attenuating NaAs-induced renal dysfunction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon-gamma plays protective roles in sodium arsenite-induced renal injury by up-regulating intrarenal multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 expression.Am J Pathol. 2006 Oct;169(4):1118-28. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060024. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 17003472 Free PMC article.
-
Exaggerated arsenic nephrotoxicity in female mice through estrogen-dependent impairments in the autophagic flux.Toxicology. 2016 Jan 2;339:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Toxicology. 2016. PMID: 26631322
-
MRP-1 expression levels determine strain-specific susceptibility to sodium arsenic-induced renal injury between C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005 Feb 15;203(1):53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2004.07.013. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15694464
-
Interferon-γ is protective in cisplatin-induced renal injury by enhancing autophagic flux.Kidney Int. 2012 Nov;82(10):1093-104. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.240. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22785177
-
Interleukin-22 in Renal Protection and Its Pathological Role in Kidney Diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 31;13:851818. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.851818. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35432360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The application of autophagy to thrombus age estimation in murine deep vein thrombosis model.Int J Legal Med. 2020 May;134(3):1061-1066. doi: 10.1007/s00414-019-02168-0. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Int J Legal Med. 2020. PMID: 31713680
-
Autophagy and Tubular Cell Death in the Kidney.Semin Nephrol. 2016 May;36(3):174-88. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2016.03.005. Semin Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27339383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy in kidney health and disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Jan 20;20(3):519-37. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5363. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 23642034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promotion of autophagy at the maturation step by IL-6 is associated with the sustained mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Aug;380(1-2):219-27. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1676-9. Epub 2013 May 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23677697
-
Crucial Involvement of IL-6 in Thrombus Resolution in Mice via Macrophage Recruitment and the Induction of Proteolytic Enzymes.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 7;10:3150. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03150. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oremland RS, Stolz JF. The ecology of arsenic. Science. 2003;300:939–944. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Liu YP, Goyer RA, Chanzar W, Waalkes MP. Metallothionein-I/II null mice are more sensitive than wild-type mice to the hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic effects of oral or injected inorganic arsenicals. Toxicol Sci. 2000;55:460–467. - PubMed
-
- Kimura A, Ishida Y, Wada T, Yokoyama H, Mukaida N, Kondo T. MRP-1 expression levels determine strain-specific susceptibility to sodium arsenic-induced renal injury between C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005;203:53–61. - PubMed
-
- Snow E. Metal carcinogenesis: mechanistic implications. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;53:31–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

