Highly diverse cyanobactins in strains of the genus Anabaena
- PMID: 20008171
- PMCID: PMC2813007
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01061-09
Highly diverse cyanobactins in strains of the genus Anabaena
Abstract
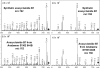
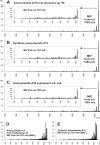
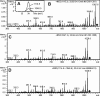
Cyanobactins are small, cyclic peptides recently found in cyanobacteria. They are formed through proteolytic cleavage and posttranslational modification of short precursor proteins and exhibit antitumor, cytotoxic, or multi-drug-reversing activities. Using genome project data, bioinformatics, stable isotope labeling, and mass spectrometry, we discovered novel cyclic peptides, anacyclamides, in 27 Anabaena strains. The lengths of the anacylamides varied greatly, from 7 to 20 amino acids. Pronounced sequence variation was also detected, and only one amino acid, proline, was present in all anacyclamides. The anacyclamides identified included unmodified proteinogenic or prenylated amino acids. We identified an 11-kb gene cluster in the genome of Anabaena sp. 90, and heterologous expression in Escherichia coli confirmed that this cluster was responsible for anacyclamide production. The discovery of anacyclamides greatly increases the structural diversity of cyanobactins.
Figures
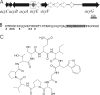
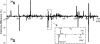
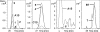
References
-
- Baba, T., and O. Schneewind. 1998. Instruments of microbial warfare: bacteriocin synthesis, toxicity and immunity. Trends Microbiol. 6:66-71. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, H. I., S. Keller, F. E. Wolter, G. J. Nicholson, G. Jung, R. D. Susmuth, and F. Jüttner. 2007. Planktocyclin, a cyclooctapeptide protease inhibitor produced by the freshwater cyanobacterium Planktothrix rubescens. J. Nat. Prod. 70:1611-1615. - PubMed
-
- Donia, M. S., B. J. Hathaway, S. Sudek, M. G. Haygood, M. J. Rosovitz, J. Ravel, and E. W. Schmidt. 2006. Natural combinatorial peptide libraries in cyanobacterial symbionts of marine ascidians. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2:729-735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

