Cutting edge: Vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated signaling in human CD45RO+ CD4+ T cells promotes Akt and ERK activation and costimulates IFN-gamma production
- PMID: 20008289
- PMCID: PMC3495980
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900397
Cutting edge: Vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated signaling in human CD45RO+ CD4+ T cells promotes Akt and ERK activation and costimulates IFN-gamma production
Abstract
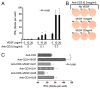
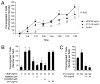
In this study, we find that CD45RO+ memory populations of CD4+ T lymphocytes express the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors KDR and Flt-1 at both the mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, by Western blot analysis, we find that VEGF increases the phosphorylation and activation of ERK and Akt within CD4+CD45RO+ T cells. These VEGF-mediated signaling responses were inhibited by a KDR-specific small interfering RNA in a VEGF receptor-expressing Jurkat T cell line and by SU5416, a pharmacological KDR inhibitor, in CD4+CD45RO+ T cells. We also find that VEGF augments mitogen-induced production of IFN-gamma in a dose-dependent manner (p < 0.001) and significantly (p < 0.05) increases directed chemotaxis of this T cell subset. Collectively, our results for the first time define a novel function for VEGF and KDR in CD45RO+ memory T cell responses that are likely of great pathophysiological importance in immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1995;1:27–31. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe H, Mamelak AJ, Wang B, Howell BG, Freed I, Esche C, Nakayama M, Nagasaki G, Hicklin DJ, Kerbel RS, Sauder DN. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (Flk-1/KDR) antibody suppresses contact hypersensitivity. Exp Dermatol. 2004;13:671–681. - PubMed
-
- Sho M, Akashi S, Kanehiro H, Hamada K, Kashizuka H, Ikeda N, Nomi T, Kuzumoto Y, Tsurui Y, Yoshiji H, et al. Function of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1/KDR in the alloimmune response in vivo. Transplantation. 2005;80:717–722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

