Involvement of the interaction of afadin with ZO-1 in the formation of tight junctions in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
- PMID: 20008323
- PMCID: PMC2836104
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.043760
Involvement of the interaction of afadin with ZO-1 in the formation of tight junctions in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
Abstract
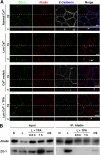
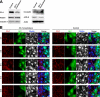
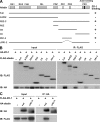
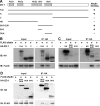
Tight junctions (TJs) and adherens junctions (AJs) are major junctional apparatuses in epithelial cells. Claudins and junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs) are major cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) at TJs, whereas cadherins and nectins are major CAMs at AJs. Claudins and JAMs are associated with ZO proteins, whereas cadherins are associated with beta- and alpha-catenins, and nectins are associated with afadin. We previously showed that nectins first form cell-cell adhesions where the cadherin-catenin complex is recruited to form AJs, followed by the recruitment of the JAM-ZO and claudin-ZO complexes to the apical side of AJs to form TJs. It is not fully understood how TJ components are recruited to the apical side of AJs. We studied the roles of afadin and ZO-1 in the formation of TJs in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells. Before the formation of TJs, ZO-1 interacted with afadin through the two proline-rich regions of afadin and the SH3 domain of ZO-1. During and after the formation of TJs, ZO-1 dissociated from afadin and associated with JAM-A. Knockdown of afadin impaired the formation of both AJs and TJs in MDCK cells, whereas knockdown of ZO-1 impaired the formation of TJs, but not AJs. Re-expression of full-length afadin restored the formation of both AJs and TJs in afadin-knockdown MDCK cells, whereas re-expression of afadin-DeltaPR1-2, which is incapable of binding to ZO-1, restored the formation of AJs, but not TJs. These results indicate that the transient interaction of afadin with ZO-1 is necessary for the formation of TJs in MDCK cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Implications of AMPK in the Formation of Epithelial Tight Junctions.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 13;19(7):2040. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072040. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30011834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperative roles of Par-3 and afadin in the formation of adherens and tight junctions.J Cell Sci. 2007 Jul 15;120(Pt 14):2352-65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03470. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17606991
-
Involvement of nectin in the localization of junctional adhesion molecule at tight junctions.Oncogene. 2002 Oct 31;21(50):7642-55. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205875. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12400007
-
Requirement of the actin cytoskeleton for the association of nectins with other cell adhesion molecules at adherens and tight junctions in MDCK cells.Genes Cells. 2004 Sep;9(9):843-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2004.00768.x. Genes Cells. 2004. PMID: 15330861
-
Interactions of the cell adhesion molecule nectin with transmembrane and peripheral membrane proteins for pleiotropic functions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Jan;65(2):253-63. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7290-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 17928952 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epithelial barrier assembly requires coordinated activity of multiple domains of the tight junction protein ZO-1.J Cell Sci. 2013 Apr 1;126(Pt 7):1565-75. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113399. Epub 2013 Feb 15. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23418357 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial integrity, junctional complexes, and biomarkers associated with intestinal functions.Tissue Barriers. 2022 Jul 3;10(3):1996830. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2021.1996830. Epub 2021 Oct 30. Tissue Barriers. 2022. PMID: 34719339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A role for ZO-1 and PLEKHA7 in recruiting paracingulin to tight and adherens junctions of epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 13;286(19):16743-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.230862. Epub 2011 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454477 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of AMPK in the Formation of Epithelial Tight Junctions.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 13;19(7):2040. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072040. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30011834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial junctions and Rho family GTPases: the zonular signalosome.Small GTPases. 2014;5(4):1-15. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973760. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25483301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Umeda K., Ikenouchi J., Katahira-Tayama S., Furuse K., Sasaki H., Nakayama M., Matsui T., Tsukita S., Furuse M. (2006) Cell 126, 741–754 - PubMed
-
- Yap A. S., Brieher W. M., Gumbiner B. M. (1997) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13, 119–146 - PubMed
-
- Tsukita S., Furuse M., Itoh M. (2001) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 285–293 - PubMed
-
- Ebnet K., Suzuki A., Ohno S., Vestweber D. (2004) J. Cell Sci. 117, 19–29 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

