Exogenous and endogenous ceramides elicit volume-sensitive chloride current in ventricular myocytes
- PMID: 20008476
- PMCID: PMC2836262
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvp399
Exogenous and endogenous ceramides elicit volume-sensitive chloride current in ventricular myocytes
Abstract
Aims: Because ceramide accumulates in several forms of cardiovascular disease and ceramide-induced apoptosis may involve the volume-sensitive Cl(-) current, I(Cl,swell), we assessed whether ceramide activates I(Cl,swell).
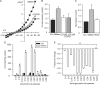
Methods and results: I(Cl,swell) was measured in rabbit ventricular myocytes by whole-cell patch clamp after isolating anion currents. Exogenous C(2)-ceramide (C(2)-Cer), a membrane-permeant short-chain ceramide, elicited an outwardly rectifying Cl(-) current in both physiological and symmetrical Cl(-) solutions that was fully inhibited by DCPIB, a specific I(Cl,swell) blocker. In contrast, the metabolically inactive C(2)-Cer analogue C(2)-dihydroceramide (C(2)-H(2)Cer) failed to activate Cl(-) current. Bacterial sphingomyelinase (SMase), which generates endogenous long-chain ceramides as was confirmed by tandem mass spectrometry, also elicited an outwardly rectifying Cl(-) current that was inhibited by DCPIB and tamoxifen, another I(Cl,swell) blocker. Bacterial SMase-induced current was partially reversed by osmotic shrinkage and fully suppressed by ebselen, a scavenger of reactive oxygen species. Outward rectification with physiological and symmetrical Cl(-) gradients, block by DCPIB and tamoxifen, and volume sensitivity are characteristics that identify I(Cl,swell). Insensitivity to C(2)-H(2)Cer and block by ebselen suggest involvement of ceramide signalling rather than direct lipid-channel interaction.
Conclusion: Exogenous and endogenous ceramide elicited I(Cl,swell) in ventricular myocytes. This may contribute to persistent activation of I(Cl,swell) and aspects of altered myocyte function in cardiovascular diseases associated with by ceramide accumulation.
Figures

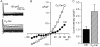



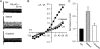

References
-
- Baumgarten CM, Browe DM, Ren Z. Swelling- and stretch-activated chloride channels in the heart: regulation and function. In: Kamkin A, Kiseleva I, editors. Mechano-Electric Feedback in the Heart: Fundamental and Clinical Aspects. Moscow: Academic Book; 2005. pp. 79–102. - PubMed
-
- Duan DY, Liu LL, Bozeat N, Huang ZM, Xiang SY, Wang GL, et al. Functional role of anion channels in cardiac diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005;26:265–278. - PubMed
-
- Hume JR, Duan D, Collier ML, Yamazaki J, Horowitz B. Anion transport in heart. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:31–81. - PubMed

