Fusobacterium nucleatum envelope protein FomA is immunogenic and binds to the salivary statherin-derived peptide
- PMID: 20008529
- PMCID: PMC2825909
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01224-09
Fusobacterium nucleatum envelope protein FomA is immunogenic and binds to the salivary statherin-derived peptide
Abstract
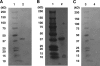
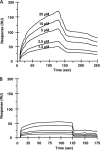
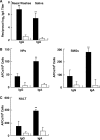
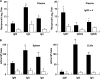
We have previously shown that one of the minimal active regions of statherin, a human salivary protein, for binding to Fusobacterium nucleatum is a YQPVPE amino acid sequence. In this study, we identified the FomA protein of F. nucleatum, which is responsible for binding to the statherin-derived YQPVPE peptide. Overlay analysis showed that a 40-kDa protein of the F. nucleatum cell envelope (40-kDa CE) specifically bound to the YQPVPE peptide. The equilibrium association constant between the affinity-purified 40-kDa CE and the YQPVPE peptide was 4.30 x 10(6). Further, the purity and amino acid sequence analyses of the purified 40-kDa CE revealed approximately 98.7% (wt/wt) purity and a high degree of homology with FomA, a major porin protein of F. nucleatum. Thus, a FomA-deficient mutant failed to bind to the YQPVPE peptide. In addition, increased levels of a FomA-specific mucosal IgA antibody (Ab) and plasma IgG and IgA Abs were seen only in mice immunized nasally with cholera toxin (CT) and the purified 40-kDa FomA protein. Interestingly, saliva from mice that received FomA plus CT as a mucosal adjuvant nasally prevented in vitro binding of F. nucleatum to statherin-coated polyvinyl chloride plates. Taken together, these results suggest that induction of specific immunity to the 40-kDa FomA protein of F. nucleatum, which specifically binds to the statherin-derived peptide, may be an effective tool for preventing the formation of F. nucleatum biofilms in the oral cavity.
Figures


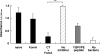
References
-
- Couch, R. B. 2004., Nasal vaccination, Escherichia coli enterotoxin, and Bell's palsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 350:860-861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

