The dynein regulatory complex is the nexin link and a major regulatory node in cilia and flagella
- PMID: 20008568
- PMCID: PMC2806320
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200908067
The dynein regulatory complex is the nexin link and a major regulatory node in cilia and flagella
Abstract
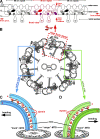
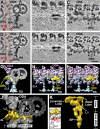
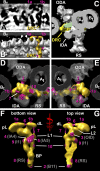
Cilia and flagella are highly conserved microtubule (MT)-based organelles with motile and sensory functions, and ciliary defects have been linked to several human diseases. The 9 + 2 structure of motile axonemes contains nine MT doublets interconnected by nexin links, which surround a central pair of singlet MTs. Motility is generated by the orchestrated activity of thousands of dynein motors, which drive interdoublet sliding. A key regulator of motor activity is the dynein regulatory complex (DRC), but detailed structural information is lacking. Using cryoelectron tomography of wild-type and mutant axonemes from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, we visualized the DRC in situ at molecular resolution. We present the three-dimensional structure of the DRC, including a model for its subunit organization and intermolecular connections that establish the DRC as a major regulatory node. We further demonstrate that the DRC is the nexin link, which is thought to be critical for the generation of axonemal bending.
Figures


References
-
- Bower R., VanderWaal K., O'Toole E., Fox L., Perrone C., Mueller J., Wirschell M., Kamiya R., Sale W.S., Porter M.E. 2009. IC138 defines a subdomain at the base of the I1 dynein that regulates microtubule sliding and flagellar motility. Mol. Biol. Cell. 20:3055–3063 10.1091/mbc.E09-04-0277 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

