A single unpaired and transcriptionally silenced X chromosome locally precludes checkpoint signaling in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line
- PMID: 20008570
- PMCID: PMC2845332
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.110338
A single unpaired and transcriptionally silenced X chromosome locally precludes checkpoint signaling in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line
Abstract
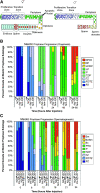
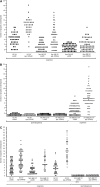
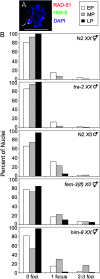
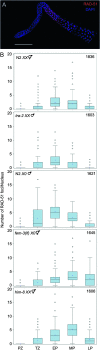
In many organisms, female and male meiosis display extensive sexual dimorphism in the temporal meiotic program, the number and location of recombination events, sex chromosome segregation, and checkpoint function. We show here that both meiotic prophase timing and germ-line apoptosis, one output of checkpoint signaling, are dictated by the sex of the germ line (oogenesis vs. spermatogenesis) in Caenorhabditis elegans. During oogenesis in feminized animals (fem-3), a single pair of asynapsed autosomes elicits a checkpoint response, yet an unpaired X chromosome fails to induce checkpoint activation. The single X in males and fem-3 worms is a substrate for the meiotic recombination machinery and repair of the resulting double strand breaks appears to be delayed compared with worms carrying paired X chromosomes. Synaptonemal complex axial HORMA domain proteins, implicated in repair of meiotic double strand breaks (DSBs) and checkpoint function, are assembled and disassembled on the single X similarly to paired chromosomes, but the central region component, SYP-1, is not loaded on the X chromosome in males. In fem-3 worms some X chromosomes achieve nonhomologous self-synapsis; however, germ cells with SYP-1-positive X chromosomes are not preferentially protected from apoptosis. Analyses of chromatin and X-linked gene expression indicate that a single X, unlike asynapsed X chromosomes or autosomes, maintains repressive chromatin marks and remains transcriptionally silenced and suggests that this state locally precludes checkpoint signaling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caenorhabditis elegans histone methyltransferase MET-2 shields the male X chromosome from checkpoint machinery and mediates meiotic sex chromosome inactivation.PLoS Genet. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002267. Epub 2011 Sep 1. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21909284 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudosynapsis and decreased stringency of meiotic repair pathway choice on the hemizygous sex chromosome of Caenorhabditis elegans males.Genetics. 2014 Jun;197(2):543-60. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.164152. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24939994 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptonemal Complex Central Region Proteins Promote Localization of Pro-crossover Factors to Recombination Events During Caenorhabditis elegans Meiosis.Genetics. 2019 Oct;213(2):395-409. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302625. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31431470 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic recombination in Caenorhabditis elegans.Chromosome Res. 2007;15(5):607-21. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1146-x. Chromosome Res. 2007. PMID: 17674149 Review.
-
DNA double strand break repair, chromosome synapsis and transcriptional silencing in meiosis.Epigenetics. 2010 May 16;5(4):255-66. doi: 10.4161/epi.5.4.11518. Epub 2010 May 16. Epigenetics. 2010. PMID: 20364103 Review.
Cited by
-
Back to the roots: segregation of univalent sex chromosomes in meiosis.Chromosoma. 2016 Jun;125(2):277-86. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0550-9. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 26511278 Review.
-
Sexual dimorphic regulation of recombination by the synaptonemal complex in C. elegans.Elife. 2023 Oct 5;12:e84538. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84538. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37796106 Free PMC article.
-
LINC complexes promote homologous recombination in part through inhibition of nonhomologous end joining.J Cell Biol. 2016 Dec 19;215(6):801-821. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201604112. Epub 2016 Dec 12. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27956467 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic Double-Strand Break Processing and Crossover Patterning Are Regulated in a Sex-Specific Manner by BRCA1-BARD1 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2020 Oct;216(2):359-379. doi: 10.1534/genetics.120.303292. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 32796008 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of Genome Integrity by Mi2 Homologs CHD-3 and LET-418 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2018 Mar;208(3):991-1007. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.300686. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29339410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alpi, A., P. Pasierbek, A. Gartner and J. Loidl, 2003. Genetic and cytological characterization of the recombination protein RAD-51 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chromosoma 112 6–16. - PubMed
-
- Aravind, L., and E. V. Koonin, 1998. The HORMA domain: a common structural denominator in mitotic checkpoints, chromosome synapsis and DNA repair. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23 284–286. - PubMed
-
- Ashley, T., A. W. Plug, J. Xu, A. J. Solari, G. Reddy et al., 1995. Dynamic changes in Rad51 distribution on chromatin during meiosis in male and female vertebrates. Chromosoma 104 19–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

