Regulation of Salmonella enterica pathogenicity island 1 by DNA adenine methylation
- PMID: 20008574
- PMCID: PMC2845334
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.108985
Regulation of Salmonella enterica pathogenicity island 1 by DNA adenine methylation
Abstract
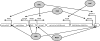
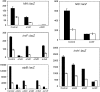
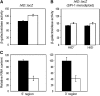
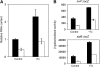
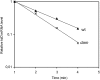
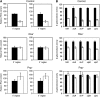
DNA adenine methylase (Dam(-)) mutants of Salmonella enterica are attenuated in the mouse model and present multiple virulence-related defects. Impaired interaction of Salmonella Dam(-) mutants with the intestinal epithelium has been tentatively correlated with reduced secretion of pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1) effectors. In this study, we show that S. enterica Dam(-) mutants contain lowered levels of the SPI-1 transcriptional regulators HilA, HilC, HilD, and InvF. Epistasis analysis indicates that Dam-dependent regulation of SPI-1 requires HilD, while HilA, HilC, and InvF are dispensable. A transcriptional hilDlac fusion is expressed at similar levels in Dam(+) and Dam(-) hosts. However, lower levels of hilD mRNA are found in a Dam(-) background, thus providing unsuspected evidence that Dam methylation might exert post-transcriptional regulation of hilD expression. This hypothesis is supported by the following lines of evidence: (i) lowered levels of hilD mRNA are found in Salmonella Dam(-) mutants when hilD is transcribed from a heterologous promoter; (ii) increased hilD mRNA turnover is observed in Dam(-) mutants; (iii) lack of the Hfq RNA chaperone enhances hilD mRNA instability in Dam(-) mutants; and (iv) lack of the RNA degradosome components polynucleotide phosphorylase and ribonuclease E suppresses hilD mRNA instability in a Dam(-) background. Our report of Dam-dependent control of hilD mRNA stability suggests that DNA adenine methylation plays hitherto unknown roles in post-transcriptional control of gene expression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A eukaryotic-like 3' untranslated region in Salmonella enterica hilD mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 May;42(9):5894-906. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku222. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24682814 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between virulence loci: regulation of Salmonella enterica pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1) by products of the std fimbrial operon.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030499. Epub 2012 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22291968 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNAs Activate Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 by Modulating mRNA Stability through the hilD mRNA 3' Untranslated Region.J Bacteriol. 2023 Jan 26;205(1):e0033322. doi: 10.1128/jb.00333-22. Epub 2022 Dec 6. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 36472436 Free PMC article.
-
Dam and its role in pathogenicity of Salmonella enterica.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2009 Aug 30;3(7):484-90. doi: 10.3855/jidc.465. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2009. PMID: 19762965 Review.
-
Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;10(1):24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17208038 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial DNA methyltransferase: A key to the epigenetic world with lessons learned from proteobacteria.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 22;14:1129437. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1129437. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37032876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in DNA methylation contribute to rapid adaptation in bacterial plant pathogen evolution.PLoS Biol. 2024 Sep 20;22(9):e3002792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002792. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39302959 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuated Salmonella typhimurium SV4089 as a potential carrier of oral DNA vaccine in chickens.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:264986. doi: 10.1155/2012/264986. Epub 2012 Jun 4. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22701301 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of SPI-1 bistability to Salmonella enterica cooperative virulence: insights from single cell analysis.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 5;8(1):14875. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33137-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30291285 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction pathway mediated by the novel regulator LoiA for low oxygen tension induced Salmonella Typhimurium invasion.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jun 2;13(6):e1006429. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006429. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28575106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbar, S., L. M. Schechter, C. P. Lostroh and C. A. Lee, 2003. AraC/XylS family members, HilD and HilC, directly activate virulence gene expression independently of HilA in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 47 715–728. - PubMed
-
- Altier, C., 2005. Genetic and environmental control of Salmonella invasion. J. Microbiol. 43 85–92. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., C. Hwang and C. A. Lee, 1995. HilA is a novel OmpR/ToxR family member that activates the expression of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes. Mol. Microbiol. 18 715–727. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., R. L. Lucas, C. Hwang and C. A. Lee, 1996. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol. Microbiol. 22 703–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

