Phase III, randomized, open-label study of daily imatinib mesylate 400 mg versus 800 mg in patients with newly diagnosed, previously untreated chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase using molecular end points: tyrosine kinase inhibitor optimization and selectivity study
- PMID: 20008622
- PMCID: PMC4979244
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.3724
Phase III, randomized, open-label study of daily imatinib mesylate 400 mg versus 800 mg in patients with newly diagnosed, previously untreated chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase using molecular end points: tyrosine kinase inhibitor optimization and selectivity study
Erratum in
- J Clin Oncol. 2010 May 1;28(13):2314
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of initial treatment with imatinib mesylate 800 mg/d (400 mg twice daily) versus 400 mg/d in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase.
Patients and methods: A total of 476 patients were randomly assigned 2:1 to imatinib 800 mg (n = 319) or 400 mg (n = 157) daily. The primary end point was the major molecular response (MMR) rate at 12 months.
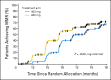
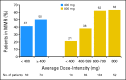
Results: At 12 months, differences in MMR and complete cytogenetic response (CCyR) rates were not statistically significant (MMR, 46% v 40%; P = .2035; CCyR, 70% v 66%; P = .3470). However, MMR occurred faster among patients randomly assigned to imatinib 800 mg/d, who had higher rates of MMR at 3 and 6 months compared with those in the imatinib 400-mg/d arm (P = .0035 by log-rank test). CCyR also occurred faster in the 800-mg/d arm (CCyR at 6 months, 57% v 45%; P = .0146). The most common adverse events were edema, gastrointestinal problems, and rash, and all were more common in patients in the 800-mg/d arm. Grades 3 to 4 hematologic toxicity also occurred more frequently in patients receiving imatinib 800 mg/d.
Conclusion: MMR rates at 1 year were similar with imatinib 800 mg/d and 400 mg/d, but MMR and CCyR occurred earlier in patients treated with 800 mg/d. Continued follow-up is needed to determine the clinical significance of earlier responses on high-dose imatinib.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN: Clinical practice guidelines in oncology—Chronic myelogenous leukemia, version 2. 2010. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Goldman JM, et al. International Randomized Study of Interferon Versus STI571 (IRIS) 7-year follow-up: Sustained survival, low rate of transformation and increased rate of major molecular response in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase treated with imatinib. Blood. 2008;112(suppl):76. abstr 186.
-
- Hughes TP, Kaeda J, Branford S, et al. Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1423–1432. - PubMed
-
- Hughes TP, Hochhaus A, Branford S, et al. Reduction of BCR-ABL transcript levels at 6, 12, and 18 months correlates with long-term outcomes on imatinib at 72 mo: An analysis from the International Randomized Study of Interferon versus STI571 (IRIS) in patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008;112(suppl):129. abstr 334.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources