Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 burden in familial Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome
- PMID: 20008652
- PMCID: PMC2864642
- DOI: 10.1001/archneurol.2009.277
Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 burden in familial Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome
Abstract
Objective: To assess the transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) burden in familial forms of Alzheimer disease (FAD) and Down syndrome (DS) to determine whether TDP-43 inclusions are also present.
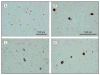
Design: Using standard immunohistochemical techniques, we examined brain tissue samples from 42 subjects with FAD and 14 with DS.
Results: We found pathological TDP-43 aggregates in 14.0% of participants (6 of 42 and 2 of 14 participants with FAD and DS, respectively). In both FAD and DS, TDP-43 immunoreactivity did not colocalize with neurofibrillary tangles. Occasionally participants with FAD or DS had TDP-43-positive neuropil threads or dots. Overall, the amygdala was most commonly affected, followed by the hippocampus, with no TDP-43 pathology in neocortical regions. A similar distribution of TDP-43 inclusions is seen in sporadic Alzheimer disease, but it differs from that seen in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.
Conclusions: Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 pathology occurs in FAD and DS, similar to that observed in sporadic Alzheimer disease. Thus, pathological TDP-43 may contribute the cognitive impairments in familial and sporadic forms of Alzheimer disease.
Figures

References
-
- Wang HY, Wang IF, Bose J, Shen CK. Structural diversity and functional implications of the eukaryotic TDP gene family. Genomics. 2004;83(1):130–139. - PubMed
-
- Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in fronto-temporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314(5796):130–133. - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, et al. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351(3):602–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

