Constitutively active AKT depletes hematopoietic stem cells and induces leukemia in mice
- PMID: 20008787
- PMCID: PMC2826762
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-229443
Constitutively active AKT depletes hematopoietic stem cells and induces leukemia in mice
Abstract
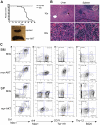
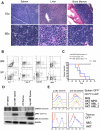
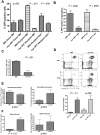
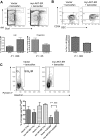
Human cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), commonly display constitutive phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) AKT signaling. However, the exact role of AKT activation in leukemia and its effects on hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are poorly understood. Several members of the PI3K pathway, phosphatase and tensin homolog (Pten), the forkhead box, subgroup O (FOXO) transcription factors, and TSC1, have demonstrated functions in normal and leukemic stem cells but are rarely mutated in leukemia. We developed an activated allele of AKT1 that models increased signaling in normal and leukemic stem cells. In our murine bone marrow transplantation model using a myristoylated AKT1 (myr-AKT), recipients develop myeloproliferative disease, T-cell lymphoma, or AML. Analysis of the HSCs in myr-AKT mice reveals transient expansion and increased cycling, associated with impaired engraftment. myr-AKT-expressing bone marrow cells are unable to form cobblestones in long-term cocultures. Rapamycin, an inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) rescues cobblestone formation in myr-AKT-expressing bone marrow cells and increases the survival of myr-AKT mice. This study demonstrates that enhanced AKT activation is an important mechanism of transformation in AML and that HSCs are highly sensitive to excess AKT/mTOR signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science. 2004;304(5670):554. - PubMed
-
- Horn S, Bergholz U, Jucker M, et al. Mutations in the catalytic subunit of class IA PI3K confer leukemogenic potential to hematopoietic cells. Oncogene. 2008;27:4096–4106. - PubMed
-
- Carpten JD, Faber AL, Horn C, et al. A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature. 2007;448(7152):439–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

