Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 Is Synthetic Lethal to Aberrant {beta}-Catenin Activation in Colon Cancer
- PMID: 20008853
- PMCID: PMC2797340
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0336
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 Is Synthetic Lethal to Aberrant {beta}-Catenin Activation in Colon Cancer
Abstract
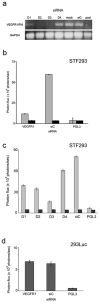
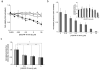
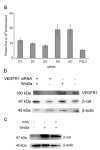
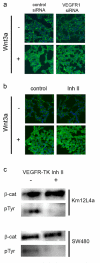
PURPOSE: The Wnt/beta-catenin (beta-cat) signaling cascade is a key regulator of development, and dysregulation of Wnt/beta-cat contributes to selected cancers, such as colorectal, breast, and hepatocellular carcinoma, through abnormal activation of Wnt target genes. To identify novel modulators of the Wnt/beta-cat pathway that may emerge as therapeutic targets, we did an unbiased high-throughput RNA interference screen. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: A synthetic oligonucleotide small interfering RNA library targeting 691 known and predicted human kinases was screened in Wnt3a-stimulated human cells in a live cell luciferase assay for modulation of Wnt/beta-cat-dependent transcription. Follow-up studies of a selected high-confidence "hit" were conducted. RESULTS: A robust quartile-based statistical analysis and secondary screen yielded several kinases worthy of further investigation, including Cdc2L1, Lmtk3, Pank2, ErbB3, and, of note, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)1/Flt1, a receptor tyrosine kinase (TK) with putative weak kinase activity conventionally believed to be a negative regulator of angiogenesis. A series of loss-of-function, genetic null, and VEGFR TK inhibitor assays further revealed that VEGFR1 is a positive regulator of Wnt signaling that functions in a glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK3beta)-independent manner as a potential synthetic lethal target in Wnt/beta-cat-addicted colon carcinoma cells. CONCLUSIONS: This unanticipated non-endothelial link between VEGFR1 TK activity and Wnt/beta-cat signaling may refine our understanding of aberrant Wnt signaling in colon carcinoma and points to new combinatorial therapeutics targeted to the tumor cell compartment, rather than angiogenesis, in the context of colon cancer. (Clin Cancer Res 2009;15(24):7529-37).
Figures

References
-
- Giles RH, van Es JH, Clevers H. Caught up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1653:1–24. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–80. - PubMed
-
- Kaelin WG., Jr. The concept of synthetic lethality in the context of anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:689–98. - PubMed
-
- Willingham AT, Deveraux QL, Hampton GM, Aza-Blanc P. RNAi and HTS: exploring cancer by systematic loss-of-function. Oncogene. 2004;23:8392–400. - PubMed
-
- Hartman JT, Garvik B, Hartwell L. Principles for the buffering of genetic variation. Science. 2001;291:1001–4. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

