The histone variant macroH2A1 marks repressed autosomal chromatin, but protects a subset of its target genes from silencing
- PMID: 20008927
- PMCID: PMC2802188
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1876110
The histone variant macroH2A1 marks repressed autosomal chromatin, but protects a subset of its target genes from silencing
Abstract
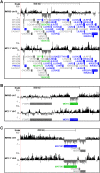
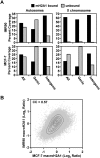
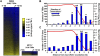
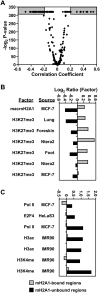
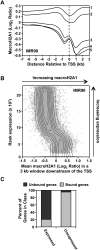
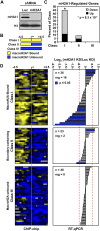
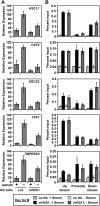
MacroH2A1 is a histone variant that is enriched on the inactive X chromosome (Xi) in mammals and is postulated to play an important, but unknown, role in the repression of gene expression. Here we show that, although macroH2A1 marks repressed autosomal chromatin, it positively regulates transcription when located in the transcribed regions of a subset of its target genes. We used chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) coupled with tiling microarrays (ChIP-chip) to determine the genomic localization of macroH2A1 in IMR90 human primary lung fibroblasts and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. The patterns of macroH2A1 deposition are largely similar across the autosomes of both cell lines. Our studies revealed a genomic localization pattern unique among histone variants; namely, the occupation by macroH2A1 of large chromatin domains (>500 kb in some cases) that contain repressive chromatin marks (e.g., histone H3 Lys 27 trimethylation). The boundaries of macroH2A1-containing domains tend to occur in promoter-proximal regions. Not all promoters, however, serve as macroH2A1 boundaries; many macroH2A1-containing chromatin domains invade the transcribed regions of genes whose products play key roles in development and cell-cell signaling. Surprisingly, the expression of a subset of these genes is positively regulated by macroH2A1. MacroH2A1 also plays a role in augmenting signal-regulated transcription, specifically for genes responsive to serum starvation. Collectively, our results document an unexpected role for macroH2A1 in the escape from heterochromatin-associated silencing and the enhancement of autosomal gene transcription.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott DW, Laszczak M, Lewis JD, Su H, Moore SC, Hills M, Dimitrov S, Ausio J. Structural characterization of macroH2A containing chromatin. Biochemistry. 2004;43:1352–1359. - PubMed
-
- Angelov D, Molla A, Perche PY, Hans F, Cote J, Khochbin S, Bouvet P, Dimitrov S. The histone variant macroH2A interferes with transcription factor binding and SWI/SNF nucleosome remodeling. Mol Cell. 2003;11:1033–1041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
