Transcriptional competence and the active marking of tissue-specific enhancers by defined transcription factors in embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 20008934
- PMCID: PMC2800090
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1861209
Transcriptional competence and the active marking of tissue-specific enhancers by defined transcription factors in embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
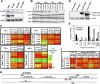
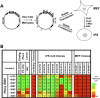
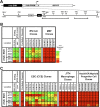
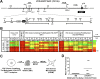
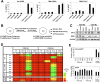
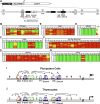
We reported previously that well-characterized enhancers but not promoters for typical tissue-specific genes, including the classic Alb1 gene, contain unmethylated CpG dinucleotides and evidence of pioneer factor interactions in embryonic stem (ES) cells. These properties, which are distinct from the bivalent histone modification domains that characterize the promoters of genes involved in developmental decisions, raise the possibility that genes expressed only in differentiated cells may need to be marked at the pluripotent stage. Here, we demonstrate that the forkhead family member FoxD3 is essential for the unmethylated mark observed at the Alb1 enhancer in ES cells, with FoxA1 replacing FoxD3 following differentiation into endoderm. Up-regulation of FoxD3 and loss of CpG methylation at the Alb1 enhancer accompanied the reprogramming of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. Studies of two genes expressed in specific hematopoietic lineages revealed that the establishment of enhancer marks in ES cells and iPS cells can be regulated both positively and negatively. Furthermore, the absence of a pre-established mark consistently resulted in resistance to transcriptional activation in the repressive chromatin environment that characterizes differentiated cells. These results support the hypothesis that pluripotency and successful reprogramming may be critically dependent on the marking of enhancers for many or all tissue-specific genes.
Figures

Comment in
-
Transcriptional competence in pluripotency.Genes Dev. 2009 Dec 15;23(24):2793-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.1881609. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 20008929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
-
- Bird A, Macleod D. Reading the DNA methylation signal. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2004;69:113–118. - PubMed
-
- Bossard P, Zaret KS. GATA transcription factors as potentiators of gut endoderm differentiation. Development. 1998;125:4909–4917. - PubMed
-
- Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, Brambrink T, Medeiros LA, Lee TI, Levine SS, Wernig M, Tajonar A, Ray MK, et al. Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2006;441:349–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
