Nearby inverted repeats fuse to generate acentric and dicentric palindromic chromosomes by a replication template exchange mechanism
- PMID: 20008937
- PMCID: PMC2800087
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1863009
Nearby inverted repeats fuse to generate acentric and dicentric palindromic chromosomes by a replication template exchange mechanism
Abstract
Gene amplification plays important roles in the progression of cancer and contributes to acquired drug resistance during treatment. Amplification can initiate via dicentric palindromic chromosome production and subsequent breakage-fusion-bridge cycles. Here we show that, in fission yeast, acentric and dicentric palindromic chromosomes form by homologous recombination protein-dependent fusion of nearby inverted repeats, and that these fusions occur frequently when replication forks arrest within the inverted repeats. Genetic and molecular analyses suggest that these acentric and dicentric palindromic chromosomes arise not by previously described mechanisms, but by a replication template exchange mechanism that does not involve a DNA double-strand break. We thus propose an alternative mechanism for the generation of palindromic chromosomes dependent on replication fork arrest at closely spaced inverted repeats.
Figures
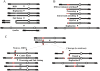
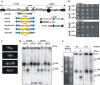
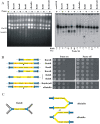
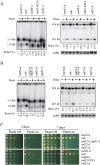
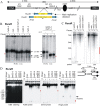
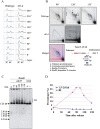
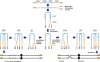
Comment in
-
Leaping forks at inverted repeats.Genes Dev. 2010 Jan 1;24(1):5-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.1884810. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20047996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilera A, Gomez-Gonzalez B. Genome instability: A mechanistic view of its causes and consequences. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:204–217. - PubMed
-
- Bahler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A, 3rd, Steever AB, Wach A, Philippsen P, Pringle JR. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast. 1998;14:943–951. - PubMed
-
- Bailey JA, Gu Z, Clark RA, Reinert K, Samonte RV, Schwartz S, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, Eichler EE. Recent segmental duplications in the human genome. Science. 2002;297:1003–1007. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Horejsi Z, Koed K, Kramer A, Tort F, Zieger K, Guldberg P, Sehested M, Nesland JM, Lukas C, et al. DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature. 2005;434:864–870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
