Active care management supported by home telemonitoring in veterans with type 2 diabetes: the DiaTel randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 20009091
- PMCID: PMC2827492
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-1012
Active care management supported by home telemonitoring in veterans with type 2 diabetes: the DiaTel randomized controlled trial
Abstract
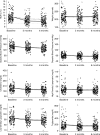
OBJECTIVE We compared the short-term efficacy of home telemonitoring coupled with active medication management by a nurse practitioner with a monthly care coordination telephone call on glycemic control in veterans with type 2 diabetes and entry A1C > or =7.5%. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS Veterans who received primary care at the VA Pittsburgh Healthcare System from June 2004 to December 2005, who were taking oral hypoglycemic agents and/or insulin for > or =1 year, and who had A1C > or =7.5% at enrollment were randomly assigned to either active care management with home telemonitoring (ACM+HT group, n = 73) or a monthly care coordination telephone call (CC group, n = 77). Both groups received monthly calls for diabetes education and self-management review. ACM+HT group participants transmitted blood glucose, blood pressure, and weight to a nurse practitioner using the Viterion 100 TeleHealth Monitor; the nurse practitioner adjusted medications for glucose, blood pressure, and lipid control based on established American Diabetes Association targets. Measures were obtained at baseline, 3-month, and 6-month visits. RESULTS Baseline characteristics were similar in both groups, with mean A1C of 9.4% (CC group) and 9.6% (ACM+HT group). Compared with the CC group, the ACM+HT group demonstrated significantly larger decreases in A1C at 3 months (1.7 vs. 0.7%) and 6 months (1.7 vs. 0.8%; P < 0.001 for each), with most improvement occurring by 3 months. CONCLUSIONS Compared with the CC group, the ACM+HT group demonstrated significantly greater reductions in A1C by 3 and 6 months. However, both interventions improved glycemic control in primary care patients with previously inadequate control.
Figures
Comment in
-
Nurse practitioner provided home telemonitoring and medication management improves glycemic control in primary care patients with type 2 diabetes more than monthly care coordination telephone call.Evid Based Nurs. 2010 Jul;13(3):74-5. doi: 10.1136/ebn1072. Evid Based Nurs. 2010. PMID: 20584825 No abstract available.
References
-
- Maciejewski ML, Maynard C: Diabetes-related utilization and costs for inpatient and outpatient services in the Veterans Administration. Diabetes Care 2004;27:B69–B73 - PubMed
-
- Miller DR, Safford MM, Pogach LM: Who has diabetes? Best estimates of diabetes prevalence in the Department of Veterans Affairs based on computerized patient data. Diabetes Care 2004;27:B10–B21 - PubMed
-
- VHA Office of Quality and Performance. Unpublished data.
-
- UKPDS Group. Effect of intensive blood glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 1998;352:854–865 [erratum 1998;352:1558] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

