EGFR signaling through an Akt-SREBP-1-dependent, rapamycin-resistant pathway sensitizes glioblastomas to antilipogenic therapy
- PMID: 20009104
- PMCID: PMC2978002
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2000446
EGFR signaling through an Akt-SREBP-1-dependent, rapamycin-resistant pathway sensitizes glioblastomas to antilipogenic therapy
Abstract
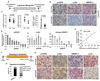
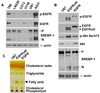
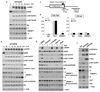
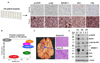
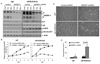
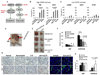
Glioblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor, is among the most lethal and difficult cancers to treat. Although epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are frequent in glioblastoma, their clinical relevance is poorly understood. Studies of tumors from patients treated with the EGFR inhibitor lapatinib revealed that EGFR induces the cleavage and nuclear translocation of the master transcriptional regulator of fatty acid synthesis, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1). This response was mediated by Akt; however, clinical data from rapamycin-treated patients showed that SREBP-1 activation was independent of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1, possibly explaining rapamycin's poor efficacy in the treatment of such tumors. Glioblastomas without constitutively active EGFR signaling were resistant to inhibition of fatty acid synthesis, whereas introduction of a constitutively active mutant form of EGFR, EGFRvIII, sensitized tumor xenografts in mice to cell death, which was augmented by the hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor atorvastatin. These results identify a previously undescribed EGFR-mediated prosurvival metabolic pathway and suggest new therapeutic approaches to treating EGFR-activated glioblastomas.
Figures
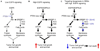
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
-
- Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, Chin L, DePinho RA, Cavenee WK. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2683–2710. - PubMed
-
- Bublil EM, Yarden Y. The EGF receptor family: spearheading a merger of signaling and therapeutics. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:124–134. - PubMed
-
- Schlessinger J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 2000;103:211–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA108633/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR03186/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050151/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA54174/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS050151/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA16672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA119347/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062422/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA62412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062407/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA108633/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA62422/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- CA 62404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA62426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA62399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA119347/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

