Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and transplantation
- PMID: 20009161
- PMCID: PMC2843931
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and transplantation
Abstract
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is an inherited disorder affecting 1 in 1,000 people and responsible for 10% of cases of the end stage renal disease (ESRD). Apart from renal manifestations, changes in other organs may be present. In the absence of contraindications, patients with ADPKD and ESRD should be referred to renal transplantation. The ADPKD patient may also need liver transplantation, or combined liver and kidney transplantation. Also, the patient with ADPKD may become a potential organ donor. The aim of our paper is to review the problems that the physicians deal with in ADPKD patients in pre- and post-transplant period.
Figures
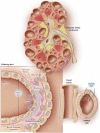

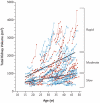
Similar articles
-
Management of ESRD in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010 Mar;17(2):164-72. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2009.12.006. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010. PMID: 20219619 Review.
-
Clinical aspects of renal transplantation in polycystic kidney disease.Clin Nephrol. 2002 Jul;58(1):16-24. doi: 10.5414/cnp58016. Clin Nephrol. 2002. PMID: 12141402
-
Concomitant nephrectomy of massively enlarged kidneys and renal transplantation in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Transplant Proc. 2005 Sep;37(7):2939-40. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.07.053. Transplant Proc. 2005. PMID: 16213267
-
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Transplant Recipients After Kidney Transplantation: A Single-center Experience.Transplant Proc. 2017 Sep;49(7):1522-1525. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2017.06.014. Transplant Proc. 2017. PMID: 28838432
-
ADPKD: clinical issues before and after renal transplantation.J Nephrol. 2016 Dec;29(6):755-763. doi: 10.1007/s40620-016-0349-7. Epub 2016 Oct 20. J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27766568 Review.
Cited by
-
Celecoxib inhibits growth of human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney cyst-lining epithelial cells through the VEGF/Raf/MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Jul;39(7):7743-53. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1611-2. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22415852 Free PMC article.
-
Deep-Red and Near-Infrared Compact Cyanine Dyes for Sensitive NAD(P)H Sensing in Live Cells and Kidney Disease Tissues.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Dec 16;7(12):8552-8564. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c01345. Epub 2024 Nov 26. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 39589839
-
Clinical outcomes of kidney transplants on patients with end-stage renal disease secondary to lupus nephritis, polycystic kidney disease and diabetic nephropathy.Colomb Med (Cali). 2016 Mar 30;47(1):51-8. Colomb Med (Cali). 2016. PMID: 27226665 Free PMC article.
-
Soy Protein Alleviates Hypertension and Fish Oil Improves Diastolic Heart Function in the Han:SPRD-Cy Rat Model of Cystic Kidney Disease.Lipids. 2016 May;51(5):635-42. doi: 10.1007/s11745-015-4095-8. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Lipids. 2016. PMID: 26626478
-
Fundamental insights into autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease from human-based cell models.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Oct;34(10):1697-1715. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-4057-5. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30215095
References
-
- Torres V, Grantham J. Cystic diseases of the kidney. In: Brenner B, editor. The kidney. Vol. 6. Saunders Elsevier; Philadelphia: 2008. pp. 1428–62.
-
- Igarashi P, Somlo S. Genetics and pathogenesis of polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2384–98. - PubMed
-
- Grantham JJ, Torres VE, Chapman AB, et al. Volume progression in polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2122–30. - PubMed
-
- Harris PC, Bae KT, Rossetti S, et al. Cyst number but not the rate of cystic growth is associated with the mutated gene in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:3013–9. - PubMed
-
- Hateboer N, van Dijk MA, Bogdanova N, et al. Comparison of phenotypes of polycystic kidney disease types 1 and 2. Lancet. 1999;353:103–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
