Recombinant alpha-actin for specific fluorescent labeling
- PMID: 20009382
- PMCID: PMC3621554
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.85.491
Recombinant alpha-actin for specific fluorescent labeling
Abstract
Until recently, actin was thought to act merely as a passive track for its motility partner, myosin, during actomyosin interactions. Yet a recent report having observed dynamical conformational changes in labeled skeletal muscle alpha-actin suggests that actin has a more active role. Because the labeling technique was still immature, however, conclusions regarding the significance of the different conformations are difficult to make. Here, we describe the preparation of fully active alpha-actin obtained from a baculovirus expression system. We developed alpha-actin recombinants, of which subdomains 1 and 2 have specific sites for fluorescent probes. This specific labeling technique offers to significantly expand the information acquired from actin studies.
Figures
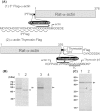
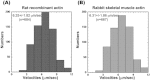

References
-
- Mounier N. and Sparrow J.C. (1997) Structural comparisons of muscle and nonmuscle actins give insights into the evolution of their functional difference. J. Mol. Evo. 44, 89–97 - PubMed
-
- Sellers J.R. (1999) Myosins Second Edition. Oxford University Press, Oxford
-
- Oda T., Iwasa M., Aihara T., Maeda Y. and Narita A. (2009) The nature of the globular- to fibrous-actin transition. Nature 457, 441–445 - PubMed
-
- Kozuka J., Yokota H., Arai Y., Ishii Y. and Yanagida T. (2006) Dynamic polymorphism of single actin molecules in the actin filament. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2, 83–86 - PubMed

