Mechanism of cadmium induced crystal defects in developing rat tooth enamel
- PMID: 20009383
- PMCID: PMC3621555
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.85.500
Mechanism of cadmium induced crystal defects in developing rat tooth enamel
Abstract
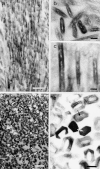
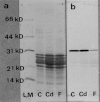
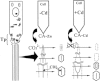
It is well known that exposure to environmental cadmium causes itai-itai (ouch-ouch) disease. However, the exact mechanism underlying this bone disease remains unresolved. By focusing on the calcification mechanism, we examined developing tooth enamel in rats exposed to cadmium to test the hypothesis that cadmium exposure may cause defects in crystal formation. Electron microscopy revealed the presence of perforated crystals in developing tooth enamel, indicating that the process of crystal nucleation may have been interrupted by cadmium exposure. Furthermore, biochemical analyses revealed that the catalytic activity of carbonic anhydrase in the immature enamel matrix declined remarkably despite the fact that quantitative reduction of this enzyme was insignificant, suggesting that the decline of catalytic activity may have resulted from the replacement of zinc with cadmium ions. Therefore, we concluded that the poor catalytic activity of cadmium-binding carbonic anhydrase might hinder the nucleation process, leading to an impairment in mineralization that causes itai-itai disease.
Figures


References
-
- Yoshiki, S., Yanagisawa, T., Kimura, M., Otaki, N., Suzuki, M. and Suda, T. (1975) Bone and kidney lesions in experimental cadmium intoxication. Arch. Environ. Health 30, 559–562 - PubMed
-
- Friberg, L., Elinder, C.G., Kjellström, T. and Nordberg, G.F. (1986) Cadmium and health: A Toxicological and Epidemiological Appraisal, Vol. 2 (Effects and Response). CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, FL, USA
-
- Ogoshi, K., Moriyama, T. and Nanzai, Y. (1989) Decrease in the mechanical strength of bones of rats administered cadmium. Arch. Toxicol. 63, 320–324 - PubMed
-
- Ogoshi, K., Nanzai, Y. and Moriyama, T. (1992) Decrease in bone strength of cadmium-treated young and old rats. Arch. Toxicol. 66, 315–320 - PubMed
-
- Sacco-Gibson, N., Chaudhry, S., Brock, A., Sickles, A.B., Patel, B., Hegstad, R. and Johnston, S. (1992) Cadmium effects on bone metabolism: accelerated resorption in ovariectomized, aged beagles. Toxicol. Appl. Phamacol. 113, 274–283 - PubMed

