Plasma nitrite response in older women to a physical function test
- PMID: 20009500
- PMCID: PMC3562699
- DOI: 10.3275/6734
Plasma nitrite response in older women to a physical function test
Abstract
Background and aims: Nitric oxide (NO) may play a critical role in facilitating the delivery of blood to active skeletal muscle, ultimately impacting functional health in older adults. Plasma nitrite is a useful marker of vascular NO bioavailability. The aim of the current investigation was to examine the effect of a widely used physical function test on plasma nitrite concentrations in older adults.
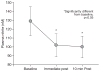
Methods: Venous blood was drawn before, immediately following, and 10 minutes following the completion of a 400-m walk test. Blood samples were added to heparin and frozen for subsequent analysis of nitrite levels using chemiluminescence.
Results: Twenty six (79±4 yrs) women participated in this study. Plasma nitrite levels decreased approximately 22% from baseline following a 400-m walk. Percent change in plasma nitrite was related to walking speed (r=-0.550, p=0.004).
Conclusions: These data suggest an alteration in plasma nitrite concentration following a functional test which may impact functional health.
Figures


References
-
- Lakatta EG, Levy D. Arterial and cardiac aging: major shareholders in cardiovascular disease enterprises: Part I: aging arteries: a “set up” for vascular disease. Circulation. 2003;107:139–46. - PubMed
-
- Paterson DH, Govindasamy D, Vidmar M, Cunningham DA, Koval JJ. Longitudinal study of determinants of dependence in an elderly population. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52:1632–8. - PubMed
-
- Cosby K, Partovi KS, Crawford JH, et al. Nitrite reduction to nitric oxide by deoxyhemoglobin vasodilates the human circulation. Nat Med. 2003;9:1498–505. - PubMed
-
- Kelm M, Preik-Steinhoff H, Preik M, Strauer BE. Serum nitrite sensitively reflects endothelial NO formation in human forearm vasculature: evidence for biochemical assessment of the endothelial L-arginine-NO pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 1999;41:765–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
