Hot-spot mutations in p110alpha of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (pI3K): differential interactions with the regulatory subunit p85 and with RAS
- PMID: 20009532
- PMCID: PMC2835815
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.9.3.10599
Hot-spot mutations in p110alpha of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (pI3K): differential interactions with the regulatory subunit p85 and with RAS
Abstract
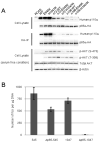
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (pI3K) signaling pathway is frequently upregulated in cancer. PIK3CA, the gene coding for the catalytic subunit p110alpha of PI3K, is mutated in about 12% of all human cancers. Most of these mutants are single amino acid substitutions that map to three positions (hot spots) in the helical or kinase domains of the enzyme. The mutant proteins show gain of enzymatic function, constitutively activate AKT signaling and induce oncogenic transformation in vitro and in animal model systems. We have shown previously that hot-spot mutations in the helical domain and kinase domain of the avian p110alpha have different requirements for interaction with the regulatory subunit p85 and with RAS-GTP. Here, we have carried out a genetic and biochemical analysis of these "hot-spot" mutations in human p110alpha. The present studies add support to the proposal that helical and kinase domain mutations in p110alpha trigger a gain of function by different molecular mechanisms. The gain of function induced by helical domain mutations requires interaction with RAS-Gtp. In contrast, the kinase domain mutation is active in the absence of RAS-Gtp binding, but depends on the interaction with p85.
Figures

References
-
- Broderick DK, Di C, Parrett TJ, Samuels YR, Cummins JM, McLendon RE, et al. Mutations of PIK3CA in anaplastic oligodendrogliomas, high-grade astrocytomas, and medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5048–50. - PubMed
-
- Campbell IG, Russell SE, Choong DY, Montgomery KG, Ciavarella ML, Hooi CS, et al. Mutation of the PIK3CA gene in ovarian and breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7678–81. - PubMed
-
- Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science. 2004;304:554. - PubMed
-
- Ikenoue T, Kanai F, Hikiba Y, Obata T, Tanaka Y, Imamura J, et al. Functional analysis of PIK3CA gene mutations in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4562–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
