A dosing/cross-development study of the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 20010555
- PMCID: PMC3291104
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2009.217
A dosing/cross-development study of the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
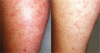
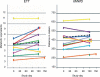
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and cancer share elements of pathophysiology. This provides an opportunity for the cross-development of anticancer agents that can be used in improving PAH care. The adaptation of new drugs across these disease populations warrants a structured approach. This study was a 16-week, phase Ib, single-center, open-label trial of the multikinase/angiogenesis inhibitor sorafenib. In order to assess the safety of sorafenib in PAH, patients with advanced but stable disease on parenteral prostanoids (with or without oral sildenafil) were initiated on treatment at the lowest active dosage administered to cancer patients: 200 mg daily. Patients underwent weekly clinical evaluations and monthly functional testing and dose escalations to a final dosage of 400 mg twice daily. Among 12 patients (10 of them women), sorafenib was well tolerated at 200 mg twice daily. The most common adverse events were moderate skin reactions on the hands and feet and alopecia. Our conclusion was therefore that this is a tolerable dosing regimen for testing the therapeutic activity of sorafenib in PAH patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sorafenib: a review of its use in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Drugs. 2009;69(2):223-40. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969020-00006. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19228077 Review.
-
Phase II clinical trial of sorafenib in metastatic medullary thyroid cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2010 May 10;28(14):2323-30. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.0068. Epub 2010 Apr 5. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20368568 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I trial of sorafenib in combination with IFN alpha-2a in patients with unresectable and/or metastatic renal cell carcinoma or malignant melanoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Mar 15;13(6):1801-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1432. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17363536 Clinical Trial.
-
Frequent dose interruptions are required for patients receiving oral kinase inhibitor therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma.Am J Clin Oncol. 2010 Jun;33(3):217-20. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e3181a650a6. Am J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19745694
-
Sorafenib: in hepatocellular carcinoma.Drugs. 2008;68(2):251-8. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200868020-00007. Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18197728 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Deterioration of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) in a Patient with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1).Case Rep Cardiol. 2019 Jul 22;2019:2987461. doi: 10.1155/2019/2987461. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31428480 Free PMC article.
-
New perspectives for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 May;163(1):125-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01164.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21175577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticipated classes of new medications and molecular targets for pulmonary arterial hypertension.Pulm Circ. 2013 Jan;3(1):226-44. doi: 10.4103/2045-8932.109940. Pulm Circ. 2013. PMID: 23662201 Free PMC article.
-
Looking to the future: a new decade of pulmonary arterial hypertension therapy.Eur Respir Rev. 2011 Dec;20(122):262-9. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00006411. Eur Respir Rev. 2011. PMID: 22130819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacologic treatments for pulmonary hypertension: exploring pharmacogenomics.Future Cardiol. 2013 May;9(3):335-49. doi: 10.2217/fca.13.6. Future Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23668740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wagenvoort C, Wagenvoort N. Pathology of Pulmonary Hypertension. 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons; New York: 1977.
-
- Wagenvoort CA, Mulder PG. Thrombotic lesions in primary plexogenic arteriopathy. Similar pathogenesis or complication? Chest. 1993;103:844–849. - PubMed
-
- Tuder RM, et al. Expression of angiogenesis-related molecules in plexiform lesions in severe pulmonary hypertension: evidence for a process of disordered angiogenesis. J. Pathol. 2001;195:367–374. - PubMed
-
- Chin KM, Rubin LJ. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008;51:1527–1538. - PubMed
-
- Humbert M, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in France: results from a national registry. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006;173:1023–1030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

