FANCM regulates DNA chain elongation and is stabilized by S-phase checkpoint signalling
- PMID: 20010692
- PMCID: PMC2829158
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.371
FANCM regulates DNA chain elongation and is stabilized by S-phase checkpoint signalling
Abstract
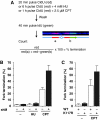
FANCM binds and remodels replication fork structures in vitro. We report that in vivo, FANCM controls DNA chain elongation in an ATPase-dependent manner. In the presence of replication inhibitors that do not damage DNA, FANCM counteracts fork movement, possibly by remodelling fork structures. Conversely, through damaged DNA, FANCM promotes replication and recovers stalled forks. Hence, the impact of FANCM on fork progression depends on the underlying hindrance. We further report that signalling through the checkpoint effector kinase Chk1 prevents FANCM from degradation by the proteasome after exposure to DNA damage. FANCM also acts in a feedback loop to stabilize Chk1. We propose that FANCM is a ringmaster in the response to replication stress by physically altering replication fork structures and by providing a tight link to S-phase checkpoint signalling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
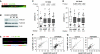
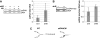

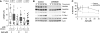


Comment in
-
FANCM: fork pause, rewind and play.EMBO J. 2010 Feb 17;29(4):703-5. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.415. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20160754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auerbach AD, Wolman SR (1976) Susceptibility of Fanconi's anaemia fibroblasts to chromosome damage by carcinogens. Nature 261: 494–496 - PubMed
-
- Azzalin CM, Lingner J (2006) The human RNA surveillance factor UPF1 is required for S phase progression and genome stability. Curr Biol 16: 433–439 - PubMed
-
- Bakker ST, van de Vrugt HJ, Rooimans MA, Oostra AB, Steltenpool J, Delzenne-Goette E, van der Wal A, van der Valk M, Joenje H, te Riele H, de Winter JP (2009) Fancm-deficient mice reveal unique features of Fanconi anemia complementation group M. Hum Mol Genet 18: 3484–3495 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

