Coordination of genomic structure and transcription by the main bacterial nucleoid-associated protein HU
- PMID: 20010798
- PMCID: PMC2816637
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2009.232
Coordination of genomic structure and transcription by the main bacterial nucleoid-associated protein HU
Abstract
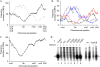
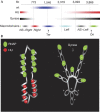
The histone-like protein HU is a highly abundant DNA architectural protein that is involved in compacting the DNA of the bacterial nucleoid and in regulating the main DNA transactions, including gene transcription. However, the coordination of the genomic structure and function by HU is poorly understood. Here, we address this question by comparing transcript patterns and spatial distributions of RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli wild-type and hupA/B mutant cells. We demonstrate that, in mutant cells, upregulated genes are preferentially clustered in a large chromosomal domain comprising the ribosomal RNA operons organized on both sides of OriC. Furthermore, we show that, in parallel to this transcription asymmetry, mutant cells are also impaired in forming the transcription foci-spatially confined aggregations of RNA polymerase molecules transcribing strong ribosomal RNA operons. Our data thus implicate HU in coordinating the global genomic structure and function by regulating the spatial distribution of RNA polymerase in the nucleoid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Azam TA, Ishihama A (1999) Twelve species of the nucleoid-associated protein from Escherichia coli. Sequence recognition specificity and DNA binding affinity. J Biol Chem 274: 33105–33113 - PubMed
-
- Azam TA, Hiraga S, Ishihama A (2000) Two types of localization of the DNA-binding proteins within the Escherichia coli nucleoid. Genes Cells 5: 613–626 - PubMed
-
- Bensaid A, Almeida A, Drlica K, Rouviere-Yaniv J (1996) Cross-talk between topoisomerase I and HU in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 256: 292–300 - PubMed
-
- Bowater RP, Chen D, Lilley DM (1994) Elevated unconstrained supercoiling of plasmid DNA generated by transcription and translation of the tetracycline resistance gene in eubacteria. Biochemistry 33: 9266–9275 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

