RNA-directed DNA methylation and plant development require an IWR1-type transcription factor
- PMID: 20010803
- PMCID: PMC2816620
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2009.246
RNA-directed DNA methylation and plant development require an IWR1-type transcription factor
Abstract
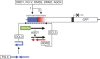
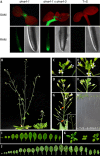
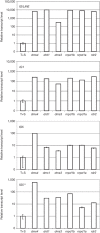
RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) in plants requires two RNA polymerase (Pol) II-related RNA polymerases, namely Pol IV and Pol V. A genetic screen designed to reveal factors that are important for RdDM in a developmental context in Arabidopsis identified DEFECTIVE IN MERISTEM SILENCING 4 (DMS4). Unlike other mutants defective in RdDM, dms4 mutants have a pleiotropic developmental phenotype. The DMS4 protein is similar to yeast IWR1 (interacts with RNA polymerase II), a conserved putative transcription factor that interacts with Pol II subunits. The DMS4 complementary DNA partly complements the K1 killer toxin hypersensitivity of a yeast iwr1 mutant, suggesting some functional conservation. In the transgenic system studied, mutations in DMS4 directly or indirectly affect Pol IV-dependent secondary short interfering RNAs, Pol V-mediated RdDM, Pol V-dependent synthesis of intergenic non-coding RNA and expression of many Pol II-driven genes. These data suggest that DMS4 might be a regulatory factor for several RNA polymerases, thus explaining its diverse roles in the plant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
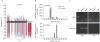
References
-
- Aouida M, Pagé N, Leduc A, Peter M, Ramotar D (2004) A genome-wide screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals altered transport as a mechanism of resistance to the anticancer drug bleomycin. Cancer Res 64: 1102–1109 - PubMed
-
- Collins S et al. (2007) Functional dissection of protein complexes involved in yeast chromosome biology using a genetic interaction map. Nature 446: 806–810 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

