A bacterial E3 ubiquitin ligase IpaH9.8 targets NEMO/IKKgamma to dampen the host NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory response
- PMID: 20010814
- PMCID: PMC3107189
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2006
A bacterial E3 ubiquitin ligase IpaH9.8 targets NEMO/IKKgamma to dampen the host NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory response
Abstract
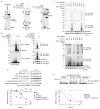
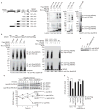
NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB) has a pivotal role in many cellular processes, including the inflammatory and immune responses and, therefore, its activation is tightly regulated by the IKK (IkappaB kinase) complex and by IkappaBalpha degradation. When Shigella bacteria multiply within epithelial cells they release peptidoglycans, which are recognized by Nod1 and stimulate the NF-kappaB pathway, thus leading to a severe inflammatory response. Here, we show that IpaH9.8, a Shigella effector possessing E3 ligase activity, dampens the NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory response to the bacterial infection in a unique way. IpaH9.8 interacts with NEMO/IKKgamma and ABIN-1, a ubiquitin-binding adaptor protein, promoting ABIN-1-dependent polyubiquitylation of NEMO. Consequently, polyubiquitylated NEMO undergoes proteasome-dependent degradation, which perturbs NF-kappaB activation. As NEMO is essential for NF-kappaB activation, we propose that the polyubiquitylation and degradation of NEMO during Shigella infection is a new bacterial strategy to modulate host inflammatory responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


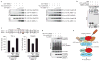
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Martnon F, Mayor A, Tchopp J. The inflammasomes: guardians of the body. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:229–265. - PubMed
-
- Li QT, Verma LM. NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nature Rev Immunol. 2002;2:725–734. - PubMed
-
- Sebban H, Yamaoka S, Courtois G. Posttranslational modifications of NEMO and its partners in NF-κB signaling. Trends in Cell Biol. 2006;16:569–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

