Hebbian reverberations in emotional memory micro circuits
- PMID: 20011142
- PMCID: PMC2751649
- DOI: 10.3389/neuro.01.027.2009
Hebbian reverberations in emotional memory micro circuits
Abstract
The study of memory in most behavioral paradigms, including emotional memory paradigms, has focused on the feed forward components that underlie Hebb's first postulate, associative synaptic plasticity. Hebb's second postulate argues that activated ensembles of neurons reverberate in order to provide temporal coordination of different neural signals, and thereby facilitate coincidence detection. Recent evidence from our groups has suggested that the lateral amygdala (LA) contains recurrent microcircuits and that these may reverberate. Additionally this reverberant activity is precisely timed with latencies that would facilitate coincidence detection between cortical and sub cortical afferents to the LA. Thus, recent data at the microcircuit level in the amygdala provide some physiological evidence in support of the second Hebbian postulate.
Keywords: amygdala; ensembles; fear; network; recurrent.
Figures
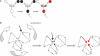


References
-
- Armony J. L., Servan-Schreiber D., Cohen J. C., LeDoux J. E. (1996). Emotion and cognition interactions in the thalalmo-cortico-amygdala network: theory and model. Cogn. Neurosci. Soc. Abstr. 3, 76
-
- Cruikshank S. J., Rose H. J., Metherate R. (2002). Auditory thalamocortical synaptic transmission in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 87, 361–384 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

