Acute intestinal pseudo-obstruction (Ogilvie's syndrome)
- PMID: 20011348
- PMCID: PMC2780141
- DOI: 10.1055/s-2005-870890
Acute intestinal pseudo-obstruction (Ogilvie's syndrome)
Abstract
Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction (ACPO), also known as Ogilvie's syndrome, is a condition characterized by massive colonic distension in the absence of mechanical obstruction. Patients presenting with Ogilvie's syndrome have underlying medical and surgical conditions predisposing them to the syndrome. Ogilvie's syndrome can often be managed by conservative therapy. However, unrecognized and untreated, the continued distension associated with Ogilvie's syndrome can lead to perforation that is associated with a high mortality rate. In this article, the pathophysiology, epidemiology, and treatment options are reviewed.
Keywords: Acute intestinal pseudo-obstruction; Ogilvie's syndrome.
Figures
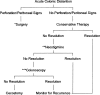
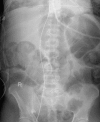
References
-
- Saunders M D, Kimmey M B. Colonic pseudo-obstruction: the dilated colon in the ICU. Semin Gastrointest Dis. 2003;14:20–27. - PubMed
-
- Law N M, Bharucha A E, Undale A S, Zinmeister A R. Cholinergic stimulation enhances colonic motor activity, transit, sensation in humans. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;281:G1228–G1237. - PubMed
-
- Ponec R J, Saunders M D, Kimmey M B. Neostigmine for the treatment of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:137–141. - PubMed
-
- Tenofsky P L, Beamer R L, Smith R S. Ogilvie syndrome as a postoperative complication. Arch Surg. 2000;135:682–687. - PubMed

