Functional disorders: rectoanal intussusception
- PMID: 20011408
- PMCID: PMC2780198
- DOI: 10.1055/s-2008-1075861
Functional disorders: rectoanal intussusception
Abstract
Rectoanal intussusception (RI) is a telescoping of the rectal wall during defecation. RI is an easily recognizable physiologic phenomenon on defecography. The management, however, is much more controversial. Two predominant hypotheses exist regarding the etiology of RI: RI as a primary disorder, and RI as a secondary phenomenon. The diagnosis may be suspected based on clinical symptoms of obstructive defecation. Diagnostic modalities include defecography as the gold standard. Dynamic pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (DPMRI) and transperineal ultrasound are attractive alternatives to defecography; however, their sensitivity is poor in comparison to the gold standard at this time. Management strategies including conservative measures such as biofeedback and surgical procedures including mucosal proctectomy (Delorme), rectopexy, and stapled transanal rectal resection (STARR) procedures have varied degrees of efficacy.
Keywords: Delorme; Rectoanal intussusception; biofeedback; defecography; rectopexy; stapled transanal rectal resection (STARR).
Figures
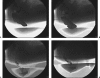
Similar articles
-
Functional Disorders: Rectoanal Intussusception.Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2017 Feb;30(1):5-11. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1593433. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2017. PMID: 28144206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stapled transanal rectal resection (STARR) to reverse the anatomic disorders of pelvic floor dyssynergia.World J Surg. 2007 Jun;31(6):1329-35. doi: 10.1007/s00268-007-9021-7. World J Surg. 2007. PMID: 17457642
-
The clinical value of magnetic resonance defecography in males with obstructed defecation syndrome.Tech Coloproctol. 2018 Mar;22(3):179-190. doi: 10.1007/s10151-018-1759-4. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Tech Coloproctol. 2018. PMID: 29512048
-
Dynamic transperineal ultrasound in the workup of men with obstructed defecation: a pilot study.Dis Colon Rectum. 2012 Sep;55(9):976-82. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0b013e31825ef8ec. Dis Colon Rectum. 2012. PMID: 22874605
-
[Indications, technique and results of the STARR procedure].Chirurg. 2016 Nov;87(11):909-917. doi: 10.1007/s00104-016-0265-3. Chirurg. 2016. PMID: 27534657 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Current applications of transperineal ultrasound in gastroenterology.World J Radiol. 2016 Apr 28;8(4):370-7. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i4.370. World J Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27158423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rectal prolapse associated with intussusception and malignancy.J Surg Case Rep. 2023 Jun 15;2023(6):rjad363. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjad363. eCollection 2023 Jun. J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37332665 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional high-resolution anorectal manometry in functional anorectal disorders: results from a large observational cohort study.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019 Apr;34(4):719-729. doi: 10.1007/s00384-019-03235-z. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019. PMID: 30706131
-
Methods of Evaluation of Anorectal Causes of Obstructed Defecation.Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2017 Feb;30(1):46-56. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1593427. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2017. PMID: 28144212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Disorders: Rectoanal Intussusception.Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2017 Feb;30(1):5-11. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1593433. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2017. PMID: 28144206 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choi J S, Hwang Y H, Salum M R, et al. Outcome and management of patients with large rectoanal intussusception. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:740–744. - PubMed
-
- Hwang Y H, Person B, Choi J S, et al. Biofeedback therapy for rectal intussusception. Tech Coloproctol. 2006;10:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Fleshman J W, Kodner I J, Fry R D. Internal intussusception of the rectum: a changing perspective. Neth J Surg. 1989;41:145–148. - PubMed
-
- Metcalf A M, Loening B V. Anorectal function and defecation dynamics in patients with rectal prolapse. Am J Surg. 1988;155:206–221. - PubMed
-
- Mellgren A, Schultz I, Johansson C, Dolk A. Internal rectal intussusception seldom develops into total rectal prolapse. Dis Colon Rectum. 1997;40:817–820. - PubMed

