Salvage hypospadias repairs
- PMID: 20011495
- PMCID: PMC2788477
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-9261.44763
Salvage hypospadias repairs
Abstract
Aim: Review of our experience and to develop an algorithm for salvage procedures in the management of hypospadias cripples and treatment of urethral strictures following hypospadias repair.
Methods: This is a retrospective review of hypospadias surgeries over a 41-month period. Out of a total 168 surgeries, 20 were salvage/re-operative repairs. In three children a Duplay repair was feasible, while in four others a variety of single-stage repairs could be done. The repair was staged in seven children - buccal mucosal grafts (BMGs) in five, buccal mucosal tube in one, and skin graft in one. Five children with dense strictures were managed by dorsal BMG inlay grafting in one, vascularized tunical onlay grafting on the ventrum in one, and a free tunical patch in one. Three children were treated by internal urethrotomy and stenting for four weeks with a poor outcome.
Results: The age of children ranged from 1.5-15 years (mean 4.5). Follow-up ranged from 3 months to 3.5 years. Excellent results were obtained in 10 children (50%) with a well-surfaced erect penis and a slit-like meatus. Glans closure could not be achieved and meatus was coronal in three. Two children developed fistulae following a Duplay repair and following a staged BMG. Three repairs failed completely - a composite repair broke down, a BMG tube stenosed with a proximal leak, and a stricture recurred with loss of a ventral free tunical graft.
Conclusions: In salvage procedures performed on hypospadias cripples, a staged repair with buccal mucosa as an inlay in the first stage followed by tubularization 4-6 months later provides good results. A simple algorithm to plan corrective surgery in failed hypospadias cases and obtain satisfactory results is devised.
Keywords: Buccal mucosal grafts; hypospadias; salvage repairs; snodgrass repair.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
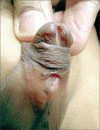
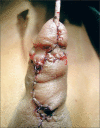


References
-
- Manzoni G, Bracka A, Palminteri E, Marrocco G. Hypospadias surgery: When, what and by whom? BJU Int. 2004;94:1188–95. - PubMed
-
- Fichtner J, Filipas D, Fisch M, Hohenfellner R, Thuroff JW. Long-term follow-up of buccal mucosal onlay graft for hypospadias repair: Analysis of complications. J Urol. 2004;172:1970–2. - PubMed
-
- Hayes MC, Malone PS. The use of a dorsal buccal mucosal graft with urethral plate incision (Snodgrass) for hypospadias salvage. BJU Int. 1999;83:508–9. - PubMed
-
- Yang SS, Chen SC, Hsieh Ch, Chen YT. Reoperative snodgrass procedure. J Urol. 2001;166:2342–45. - PubMed
-
- Snodgrass W. Does tubularised incised plate hypospadias repairs create neourethral strictures? J Urol. 1999;162:1159–61. - PubMed

