A phosphoinositide 3-kinase/phospholipase Cgamma1 pathway regulates fibroblast growth factor-induced capillary tube formation
- PMID: 20011604
- PMCID: PMC2788267
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008285
A phosphoinositide 3-kinase/phospholipase Cgamma1 pathway regulates fibroblast growth factor-induced capillary tube formation
Abstract
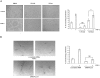
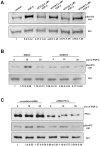
Background: The fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are key regulators of embryonic development, tissue homeostasis and tumour angiogenesis. Binding of FGFs to their receptor(s) results in activation of several intracellular signalling cascades including phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and phospholipase C (PLC)gamma1. Here we investigated the basic FGF (FGF-2)-mediated activation of these enzymes in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and defined their role in FGF-2-dependent cellular functions.
Methodology/principal findings: We show that FGF-2 activates PLCgamma1 in HUVECs measured by analysis of total inositol phosphates production upon metabolic labelling of cells and intracellular calcium increase. We further demonstrate that FGF-2 activates PI3K, assessed by analysing accumulation of its lipid product phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-P(3) using TLC and confocal microscopy analysis. PI3K activity is required for FGF-2-induced PLCgamma1 activation and the PI3K/PLCgamma1 pathway is involved in FGF-2-dependent cell migration, determined using Transwell assay, and in FGF-2-induced capillary tube formation (tubulogenesis assays in vitro). Finally we show that PI3K-dependent PLCgamma1 activation regulates FGF-2-mediated phosphorylation of Akt at its residue Ser473, determined by Western blotting analysis. This occurs through protein kinase C (PKC)alpha activation since dowregulation of PKCalpha expression using specific siRNA or blockade of its activity using chemical inhibition affects the FGF-2-dependent Ser473 Akt phosphorylation. Furthermore inhibition of PKCalpha blocks FGF-2-dependent cell migration.
Conclusion/significance: These data elucidate the role of PLCgamma1 in FGF-2 signalling in HUVECs demonstrating its key role in FGF-2-dependent tubulogenesis. Furthermore these data unveil a novel role for PLCgamma1 as a mediator of PI3K-dependent Akt activation and as a novel key regulator of different Akt-dependent processes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
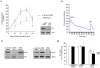
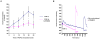
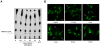
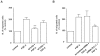
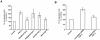
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway by inositol pentakisphosphate results in antiangiogenic and antitumor effects.Cancer Res. 2005 Sep 15;65(18):8339-49. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0121. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16166311
-
Water extract of Korean red ginseng stimulates angiogenesis by activating the PI3K/Akt-dependent ERK1/2 and eNOS pathways in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Sep;30(9):1674-9. doi: 10.1248/bpb.30.1674. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007. PMID: 17827719
-
Nerve growth factor induces endothelial cell invasion and cord formation by promoting matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway and AP-2 transcription factor.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 19;282(42):30485-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701081200. Epub 2007 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17666398
-
Recent advances in understanding the molecular role of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C gamma 1 as an emerging onco-driver and novel therapeutic target in human carcinogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Dec;1876(2):188619. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188619. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34454048 Review.
-
Role of phospholipase C in cell invasion and metastasis.Adv Biol Regul. 2013 Sep;53(3):309-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2013.07.006. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Adv Biol Regul. 2013. PMID: 23925006 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone Demethylase KDM5C Drives Prostate Cancer Progression by Promoting EMT.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 8;14(8):1894. doi: 10.3390/cancers14081894. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454801 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of collagen-rich extracellular matrix on the intracellular delivery of glycol chitosan nanoparticles in human lung fibroblasts.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Aug 21;12:6089-6105. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S138129. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28860768 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 as an Antifibrotic: Antagonism of Myofibroblast Differentiation and Suppression of Pro-Fibrotic Gene Expression.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017 Dec;38:49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 23. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017. PMID: 28967471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo missense variants in phosphatidylinositol kinase PIP5KIγ underlie a neurodevelopmental syndrome associated with altered phosphoinositide signaling.Am J Hum Genet. 2023 Aug 3;110(8):1377-1393. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2023.06.012. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Am J Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 37451268 Free PMC article.
-
The naturally processed CD95L elicits a c-yes/calcium/PI3K-driven cell migration pathway.PLoS Biol. 2011 Jun;9(6):e1001090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001090. Epub 2011 Jun 21. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21713032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653–660. - PubMed
-
- Risau W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature. 1997;386:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Davis-Smyth T. The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev. 1997;18:4–25. - PubMed
-
- Cross M J, Claesson-Welsh L. FGF and VEGF function in angiogenesis: signalling pathways, biological responses and therapeutic inhibition. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:201–207. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407:249–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

