BOL-303242-X, a novel selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist, with full anti-inflammatory properties in human ocular cells
- PMID: 20011631
- PMCID: PMC2790480
BOL-303242-X, a novel selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist, with full anti-inflammatory properties in human ocular cells
Abstract
Purpose: BOL-303242-X is a novel selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist under clinical evaluation for the treatment of inflammatory skin and eye diseases. Data from in vitro and in vivo studies suggest an improved side-effect profile of this compound compared to classical glucocorticoids. The aim of this study was to determine the anti-inflammatory effect of BOL-303242-X in ocular cells.
Methods: Four primary human ocular cell cultures, including human conjunctival fibroblasts (HConFs), human corneal epithelial cells (HCEpiCs), human optic nerve astrocytes (HONAs), and human retinal endothelial cells (HRECs), as well as a human monocytic cell line, THP-1, were challenged with either lipopolysacharide (LPS) or interleukin-1ss (IL-1ss). Luminex technology was used to determine the effect of BOL-303242-X on LPS- or IL-1ss-induced cytokine release and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) levels. Effects of BOL-303242-X on nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HCEpiCs were also assessed by measuring inhibitory kappa B protein-alpha (IkappaB-alpha), phosphorylated p65 NFkappaB, and MAPK levels by western blotting. Dexamethasone (DEX) or triamcinolone acetonide (TA) was used as the control.
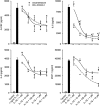
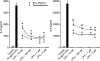
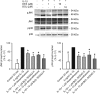
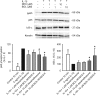
Results: LPS or IL-1ss induced multiple cytokine release in all cell types studied. BOL-303242-X significantly reduced LPS- or IL-1ss-induced inflammatory cytokine release in a dose-dependent manner, including granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), IL-1ss, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12p40, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). BOL-303242-X showed activity and potency comparable to that observed for DEX or TA. A statistically significant inhibitory effect of BOL-303242-X was observed at doses ranging from 1 to 100 nM in HConFs, HCEpiCs, HONAs, and THP-1. The IC(50) values for these effects were in the low nM range. BOL-303242-X also significantly reduced LPS-induced IL-1ss release and ICAM-1 levels in HRECs. Furthermore, BOL-303242-X inhibited IL-1ss-induced decreases in IkappaB-alpha levels, as well as IL-1ss-induced phosphorylation of NFkappaB, p38, and c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) MAPKs in HCEpiCs.
Conclusions: BOL-303242-X acts as a potent anti-inflammatory agent in various primary human ocular cells with similar activity and potency compared to classical steroids. Results also suggest that MAPK (p38 and JNK) and NFkappaB signaling pathways are involved in the anti-inflammatory properties of BOL-303242-X in HCEpiCs. An improved side effect profile of this novel SEGRA compound has been reported recently. Thus, BOL-303242-X may provide a new option for the treatment of ophthalmic conditions with an inflammatory component.
Figures

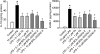
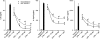
Similar articles
-
Mapracorat, a novel selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist, inhibits hyperosmolar-induced cytokine release and MAPK pathways in human corneal epithelial cells.Mol Vis. 2010 Sep 2;16:1791-800. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20824100 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-allergic effects of mapracorat, a novel selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist, in human conjunctival fibroblasts and epithelial cells.Mol Vis. 2013 Jul 19;19:1515-25. Print 2013. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 23878502 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of besifloxacin, a novel fluoroquinolone, in primary human corneal epithelial cells.Curr Eye Res. 2008 Nov;33(11):923-32. doi: 10.1080/02713680802478704. Curr Eye Res. 2008. PMID: 19085374
-
Mapracorat, a novel non-steroidal selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2014;13(5):289-98. doi: 10.2174/1871528113666141106101356. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 25373600 Review.
-
Puerarin: A review of its mechanisms of action and clinical studies in ophthalmology.Phytomedicine. 2022 Dec;107:154465. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154465. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36166943 Review.
Cited by
-
Eosinophil as a cellular target of the ocular anti-allergic action of mapracorat, a novel selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist.Mol Vis. 2011;17:3208-23. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 22194647 Free PMC article.
-
11β-HSD1 is the major regulator of the tissue-specific effects of circulating glucocorticoid excess.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 17;111(24):E2482-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323681111. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24889609 Free PMC article.
-
A method to extract cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases from Schirmer strips and analyze using Luminex.Mol Vis. 2011 Apr 27;17:1056-63. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21552500 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive and LPS-induced expression of MCP-1 and IL-8 by human uveal melanocytes in vitro and relevant signal pathways.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Aug 14;55(9):5760-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14685. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 25125602 Free PMC article.
-
Mapracorat, a novel selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist, inhibits hyperosmolar-induced cytokine release and MAPK pathways in human corneal epithelial cells.Mol Vis. 2010 Sep 2;16:1791-800. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20824100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barabino S, Dana MR. Dry eye syndromes. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2007;92:176–84. - PubMed
-
- Leonardi A, De Dominicis C, Motterle L. Immunopathogenesis of ocular allergy: a schematic approach to different clinical entities. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;7:429–35. - PubMed
-
- Butrus S, Portela R. Ocular allergy: diagnosis and treatment. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2005;18:485–92. - PubMed
-
- Nowak JZ. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD): pathogenesis and therapy. Pharmacol Rep. 2006;58:353–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
