Biphasic dose response in low level light therapy
- PMID: 20011653
- PMCID: PMC2790317
- DOI: 10.2203/dose-response.09-027.Hamblin
Biphasic dose response in low level light therapy
Abstract
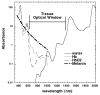
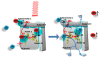
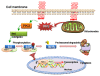
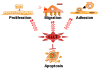
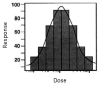
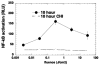
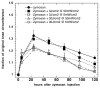
The use of low levels of visible or near infrared light for reducing pain, inflammation and edema, promoting healing of wounds, deeper tissues and nerves, and preventing cell death and tissue damage has been known for over forty years since the invention of lasers. Despite many reports of positive findings from experiments conducted in vitro, in animal models and in randomized controlled clinical trials, LLLT remains controversial in mainstream medicine. The biochemical mechanisms underlying the positive effects are incompletely understood, and the complexity of rationally choosing amongst a large number of illumination parameters such as wavelength, fluence, power density, pulse structure and treatment timing has led to the publication of a number of negative studies as well as many positive ones. A biphasic dose response has been frequently observed where low levels of light have a much better effect on stimulating and repairing tissues than higher levels of light. The so-called Arndt-Schulz curve is frequently used to describe this biphasic dose response. This review will cover the molecular and cellular mechanisms in LLLT, and describe some of our recent results in vitro and in vivo that provide scientific explanations for this biphasic dose response.
Figures





References
-
- Ad N, Oron U. Impact of low level laser irradiation on infarct size in the rat following myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2001;80:109–16. - PubMed
-
- Agaiby AD, Ghali LR, Wilson R, Dyson M. Laser modulation of angiogenic factor production by T-lymphocytes. Lasers Surg Med. 2000;26:357–63. - PubMed
-
- Aimbire F, Albertini R, Pacheco MT, Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Leonardo PS, Iversen VV, Lopes-Martins RA, Bjordal JM. Low-level laser therapy induces dose-dependent reduction of TNFalpha levels in acute inflammation. Photomed Laser Surg. 2006;24:33–7. - PubMed
-
- al-Watban FA, Andres BL. The effect of He-Ne laser (632.8 nm) and Solcoseryl in vitro. Lasers Med Sci. 2001;16:267–75. - PubMed
-
- Alexandratou E, Yova D, Handris P, Kletsas D, Loukas S. Human fibroblast alterations induced by low power laser irradiation at the single cell level using confocal microscopy. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2002;1:547–52. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

